The Female Reproductive System Complete Anatomy

The Female Reproductive System Complete Anatomy Female anatomy includes the internal and external structures, including those responsible for hormones, reproduction, and sexual activity. the female reproductive system is essential for hormone regulation, sexual pleasure, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and more. the main parts of the female anatomy can be broken up into external and internal parts. The major organs of the female reproductive system include: vagina: this muscular tube receives the penis during intercourse and through it a baby leaves the uterus during childbirth. uterus: this.
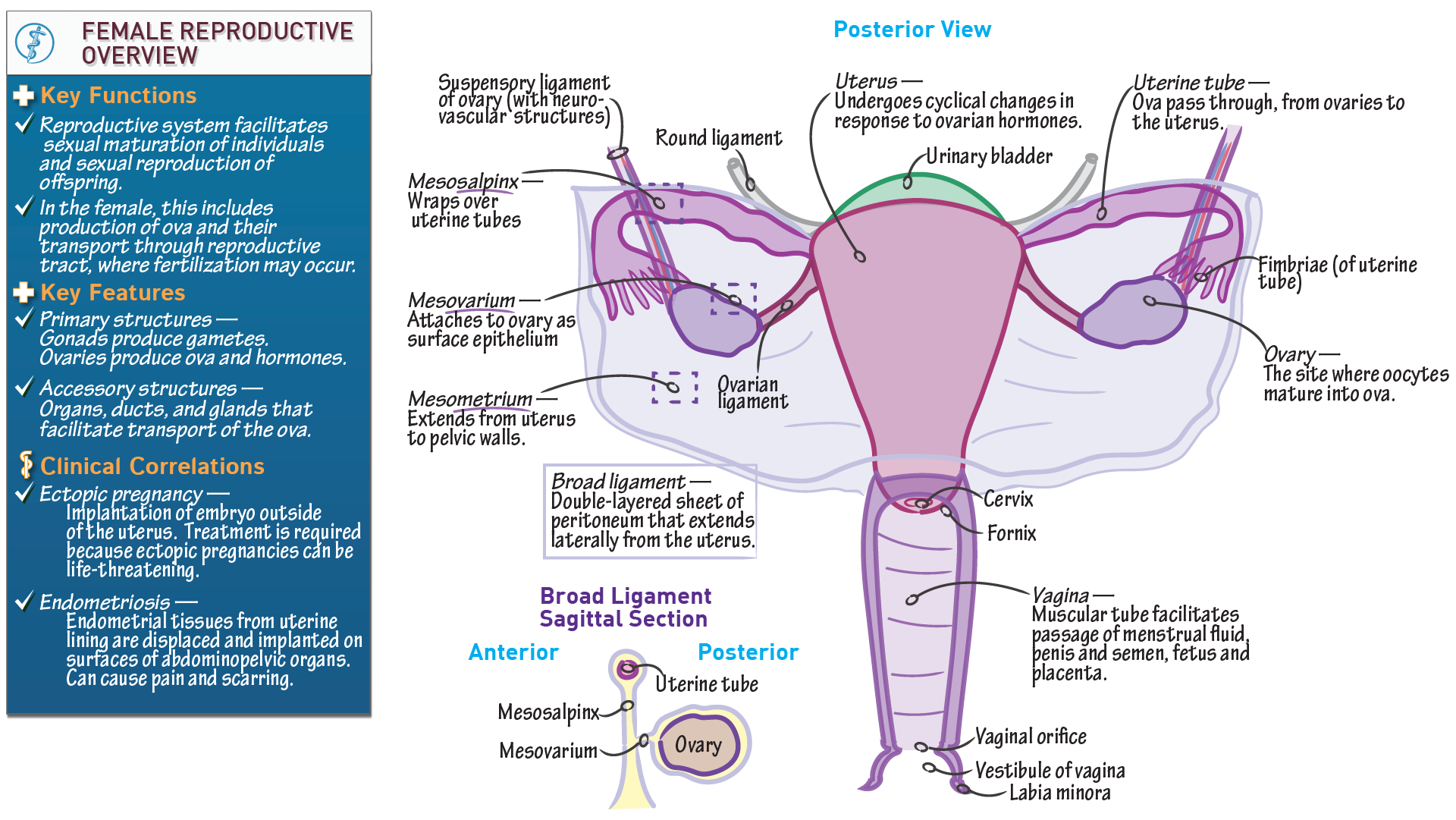
Anatomy Physiology Anatomical Overview Of The Female Reproductive Systemо In humans, female and male reproductive systems work together to reproduce. there are two kinds of sex cells — sperm and eggs. when a sperm meets an egg, it can fertilize it and create a zygote. this zygote eventually becomes a fetus. both a sperm and an egg are needed for human reproduction. The uterus or womb is the major female reproductive organ. the uterus provides mechanical protection, nutritional support, and waste removal for the developing embryo (weeks 1 to 8) and fetus (from week 9 until the delivery). in addition, contractions in the muscular wall of the uterus are important in pushing out the fetus at the time of birth. Uterus. cervix and vagina. clitoris. vulva. summary. the female reproductive organs include several key structures, such as the ovaries, uterus, vagina, and vulva. the functions of these organs. Internal reproductive organs. uterus (womb) cervix. fallopian tubes. ovaries. vagina. the uterus, or womb, is a hollow organ located centrally in the pelvis. it houses the developing fetus during pregnancy. the lower portion of the uterus is called the cervix and opens into the vagina or birth canal.
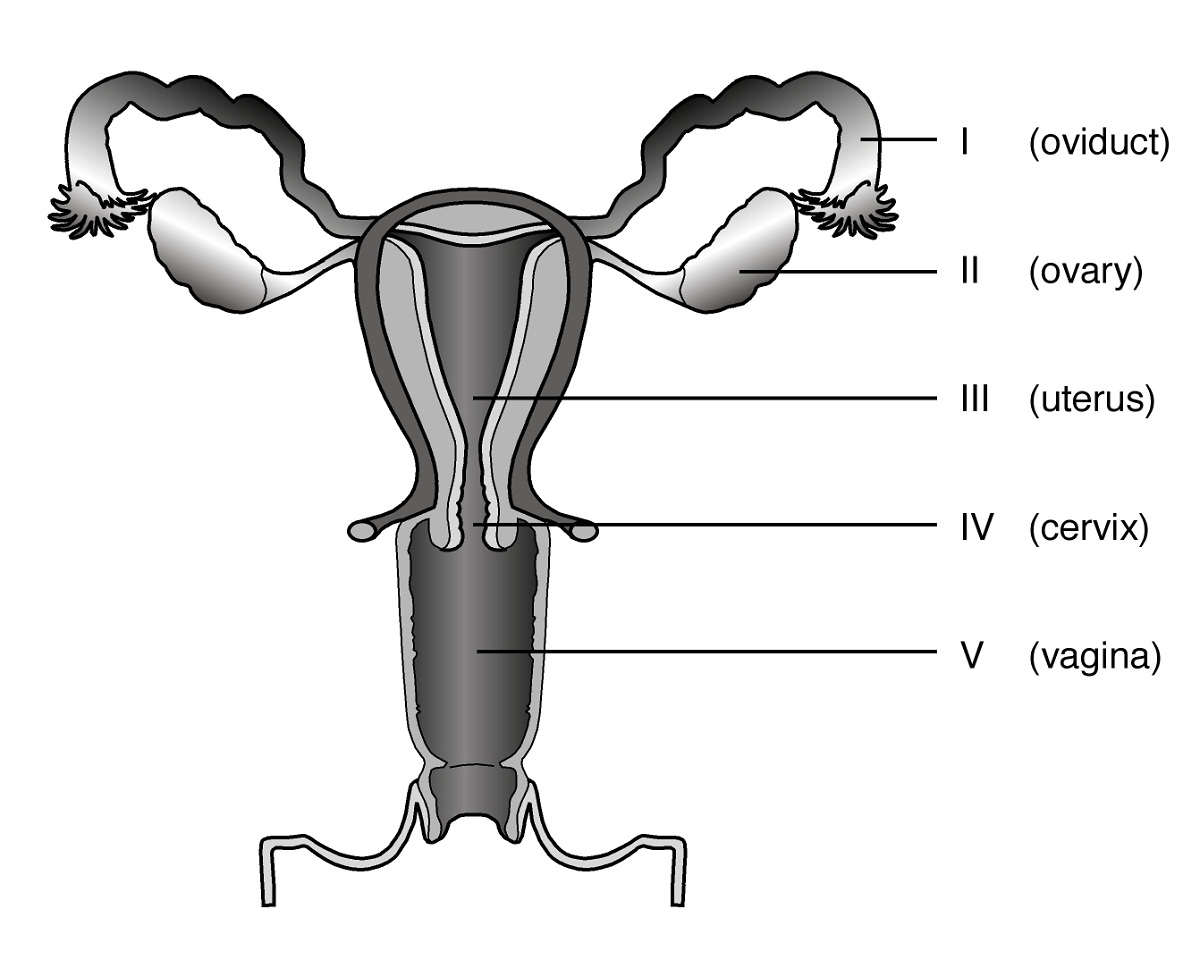
Diagrams Of Female Reproductive System 101 Diagrams Uterus. cervix and vagina. clitoris. vulva. summary. the female reproductive organs include several key structures, such as the ovaries, uterus, vagina, and vulva. the functions of these organs. Internal reproductive organs. uterus (womb) cervix. fallopian tubes. ovaries. vagina. the uterus, or womb, is a hollow organ located centrally in the pelvis. it houses the developing fetus during pregnancy. the lower portion of the uterus is called the cervix and opens into the vagina or birth canal. Toggle anatomy system. the female reproductive system includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, vulva, mammary glands and breasts. these organs are involved in the production and transportation of gametes and the production of sex hormones. the female reproductive system also facilitates the fertilization of ova by sperm and. Contributors. the female reproductive system includes all of the internal and external organs that help with reproduction. the internal sex organs are the ovaries, which are the female gonads, the fallopian tubes, two muscular tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus, and the uterus, which is the strong muscular sack that a fetus can.
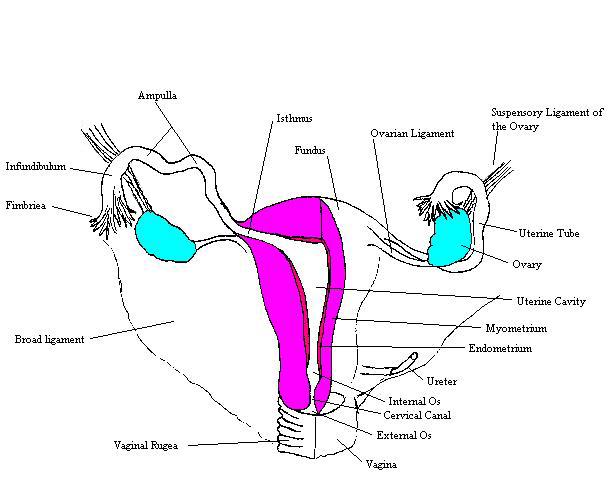
Femalereproductionantcomplete Toggle anatomy system. the female reproductive system includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, vulva, mammary glands and breasts. these organs are involved in the production and transportation of gametes and the production of sex hormones. the female reproductive system also facilitates the fertilization of ova by sperm and. Contributors. the female reproductive system includes all of the internal and external organs that help with reproduction. the internal sex organs are the ovaries, which are the female gonads, the fallopian tubes, two muscular tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus, and the uterus, which is the strong muscular sack that a fetus can.

Comments are closed.