Spanish Subject Pronouns Explained
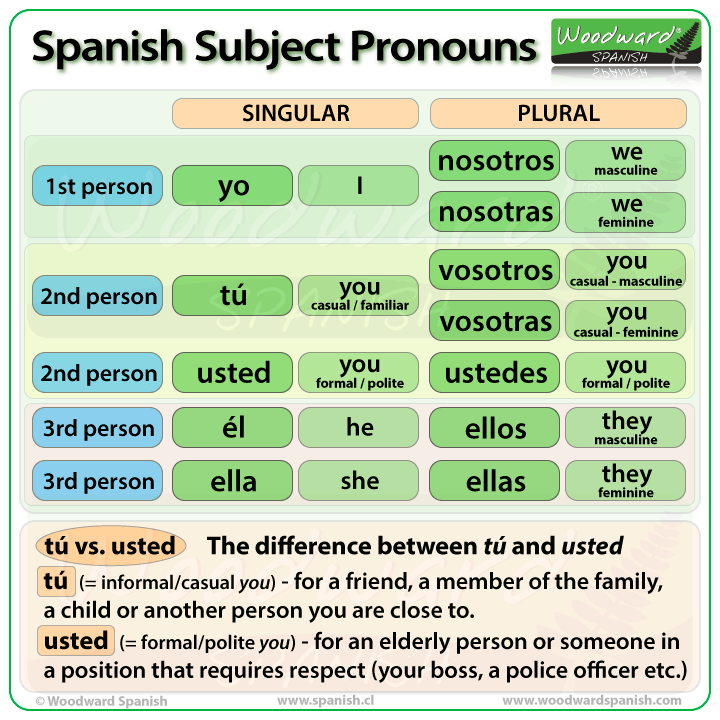
Subject Pronouns In Spanish Subject pronouns in spanish: explained for beginners. adrian in basic grammar. subject pronouns in spanish, or los pronombres personales, are used as the subject of a sentence. their main function is to replace the noun that carries out the sentence’s main action. today we’ll cover everything you need to know about the spanish subject pronouns. The spanish subject pronouns explained. yo, tú, él, ella …. these spanish subject pronouns are bound to look familiar to anyone who has cracked open a beginner’s spanish book. but after reading this post, you will know to use spanish personal pronouns like a true native speaker (no matter where you travel). let me guide you through each.

Spanish Subject Pronouns Guide Chart Examples Practice Subject pronouns often replace a subject noun and can be classified several different ways: by person (first, second, or third person), number (singular or plural), gender (male or female), and formality (formal or informal). luckily, we've provided a snazzy chart so you have all the spanish subject pronouns in one place. Spanish conjugations have different endings for each subject pronoun. so, unlike english, subject pronouns in spanish can usually be omitted because the conjugation often indicates who the subject is. take note: notice that spanish has a formal and informal ‘you’. although they have the same translation, these pronouns are applied in. Él – he. ella – she. usted (formal) – you. plural subject pronouns. nosotros nosotras – we. vosotros vosotras (spain) – you. ellos ellas – they. ustedes – you. take note: keep in mind that, in latin america, the pronoun vosotros is never used. Spanish subject pronouns or personal pronouns are words used to replace a noun (un sustantivo) working as the subject of a sentence. generally speaking, they give us information about the subject, including its gender (masculine feminine) and number (singular plural). the pronoun “Él”, for instance, will replace a man’s name, just as in.

Comments are closed.