Solved Locate The Centroid Of The Area Under The Curve X C

Solved 26 A Locate The Centroid Of The Area Under The Curve Cheg Centre of mass (centroid) for a thin plate. 1) rectangle: the centroid is (obviously) going to be exactly in the centre of the plate, at (2, 1). 2) more complex shapes:. we divide the complex shape into rectangles and find `bar(x)` (the x coordinate of the centroid) and `bar(y)` (the y coordinate of the centroid) by taking moments about the y and x coordinates respectively. Figure 17.2.2: the procedure for calculating the x coordinate of the centroid. to find the y coordinate of the of the centroid, we have a similar process, but because we are moving along the y axis, the value da is the equation describing the width of the shape times the rate at which we are moving along the y axis (dy).
Solved 3 Locate The Centroid Of The Area Under The Curve Xођ Integration process. determining the centroid of a area using integration involves finding weighted average values ˉx and ˉy, by evaluating these three integrals, a = ∫da, qx = ∫ˉyel da qy = ∫ˉxel da, where. da is a differential bit of area called the element. a is the total area enclosed by the shape, and is found by evaluating the. Table of contents. integration formulas. steps for finding centroid using integration formulas. composite areas. steps to find the centroid of composite areas. example 1: centroid of a right triangle using integration formulas. example 2: centroid of semicircle using integration formulas. example 3: centroid of a tee section. Solution2. this solution demonstrates solving integrals using horizontal rectangular strips. set the slider on the diagram to \ ( (b x)\;dy\) to see a representative element. set up the integrals. as before, the triangle is bounded by the \ (x\) axis, the vertical line \ (x = b\text {,}\) and the line. Learn how to find the centroid of an area under a curve with desmos, the free online graphing calculator. try it yourself and discover more math tools.

Solved Locate The Centroid Of The Area Under The Curve Chegg Solution2. this solution demonstrates solving integrals using horizontal rectangular strips. set the slider on the diagram to \ ( (b x)\;dy\) to see a representative element. set up the integrals. as before, the triangle is bounded by the \ (x\) axis, the vertical line \ (x = b\text {,}\) and the line. Learn how to find the centroid of an area under a curve with desmos, the free online graphing calculator. try it yourself and discover more math tools. The calculus calculator is a powerful online tool designed to assist users in solving various calculus problems efficiently. here's how to make the most of its capabilities: begin by entering your mathematical expression into the above input field, or scanning it with your camera. choose the specific calculus operation you want to perform, such. Case 1: curves which are entirely above the x axis. x f (x) a b y x y = f (x) Δ. the curve y = f (x), completely above the x axis. shows a "typical" rectangle, Δx wide and y high. in this case, we find the area by simply finding the integral: \displaystyle\text {area}= {\int { {a}}^ { {b}}} f { {\left ( {x}\right)}} {\left. {d} {x}\right.}.
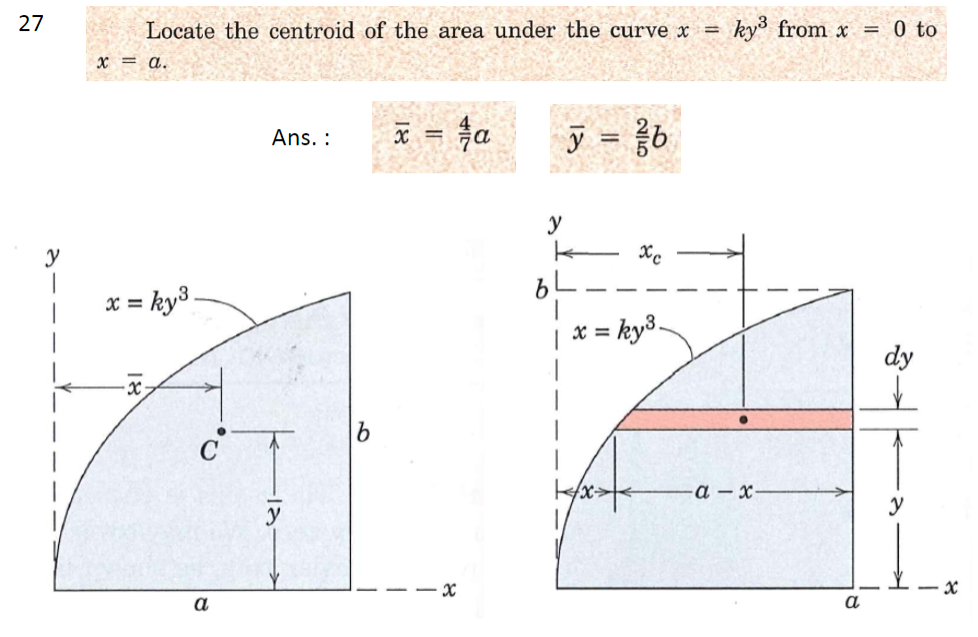
Solved 26 A Locate The Centroid Of The Area Under The Curve Cheg The calculus calculator is a powerful online tool designed to assist users in solving various calculus problems efficiently. here's how to make the most of its capabilities: begin by entering your mathematical expression into the above input field, or scanning it with your camera. choose the specific calculus operation you want to perform, such. Case 1: curves which are entirely above the x axis. x f (x) a b y x y = f (x) Δ. the curve y = f (x), completely above the x axis. shows a "typical" rectangle, Δx wide and y high. in this case, we find the area by simply finding the integral: \displaystyle\text {area}= {\int { {a}}^ { {b}}} f { {\left ( {x}\right)}} {\left. {d} {x}\right.}.
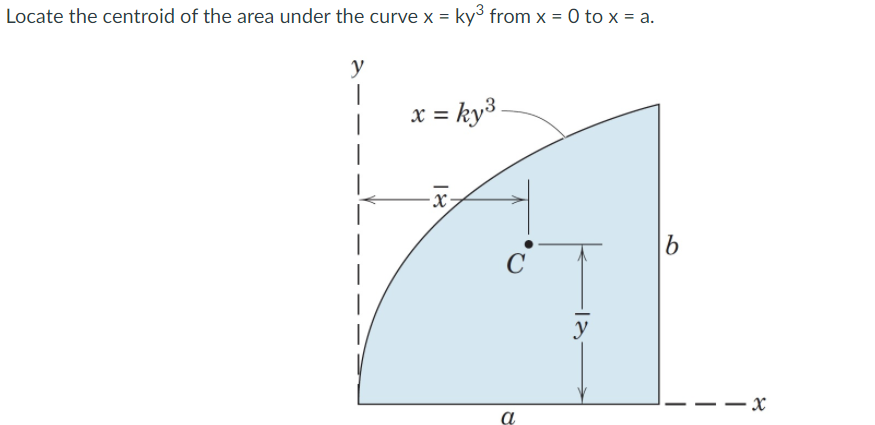
Solved Locate The Centroid Of The Area Under The Curve X C

Comments are closed.