Plant Responses To Heat Stress Cid Bio Science

Plant Responses To Heat Stress Cid Bio Science Heat stress affects crop development, growth, and productivity. plants have adaptive responses for either avoidance or tolerance of heat stress. the plant responds to heat, which can be molecular, biochemical, cellular, physiological, and morphological, and is being used by scientists to develop new cultivars for the future. High temperature is a major abiotic stress that limits the growth and production of plants. therefore, the plant response to heat stress (hs) has been a focus of research. however, the plant response to hs involves complex physiological traits and molecular or gene networks that are not fully understood. here, we review recent progress in the.

Plant Responses To Heat Stress Cid Bio Science Plants respond to heat stress: the intensity of heat, time, and type of crop all influence plant sensitivity to ht. the most prevalent impact of heat stress. is reported in table (1). intense ht. The heat stress response is characterized by inhibition of normal transcription and translation, higher expression of heat shock proteins (hsps) and induction of thermotolerance. if stress is too severe, signaling pathways leading to apoptotic cell death are also activated. as molecular chaperones, hsps provide protection to cells against the. Calcium elevation initiates heat signal transduction. changes in membrane status are always regarded as the initial responses of plants to hs, followed by activation of receptors, which subsequently contribute to increases in cytosolic ca 2 and protein translocation, among other effects. Global climate change is predicted to result in increased yield losses of agricultural crops caused by environmental conditions. in particular, heat and drought stress are major factors that negatively affect plant development and reproduction, and previous studies have revealed how these stresses induce plant responses at physiological and molecular levels.
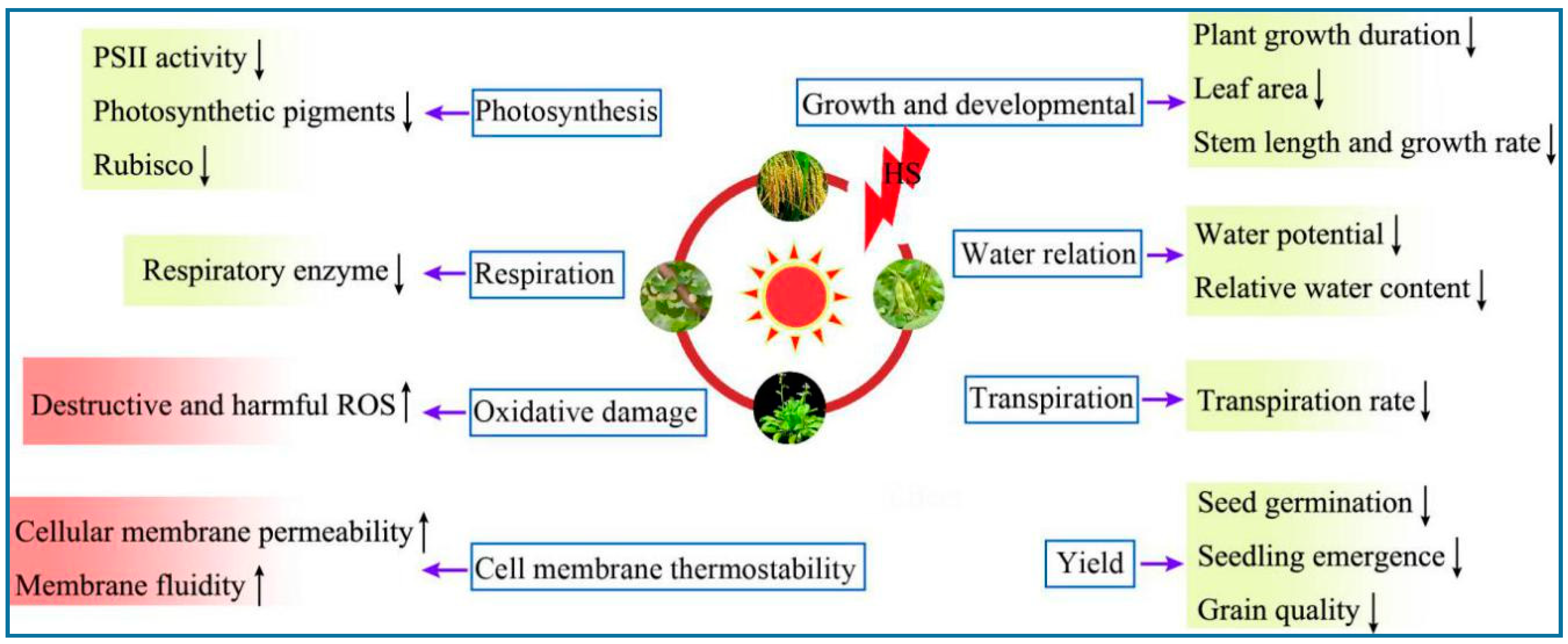
Ijms Free Full Text Plant Responses To Heat Stress Physiology Transcription Calcium elevation initiates heat signal transduction. changes in membrane status are always regarded as the initial responses of plants to hs, followed by activation of receptors, which subsequently contribute to increases in cytosolic ca 2 and protein translocation, among other effects. Global climate change is predicted to result in increased yield losses of agricultural crops caused by environmental conditions. in particular, heat and drought stress are major factors that negatively affect plant development and reproduction, and previous studies have revealed how these stresses induce plant responses at physiological and molecular levels. 5.2 heat stress response and tolerance mechanisms. plants employ complex molecular mechanisms to adapt to heat stress, including signal pathways, metabolite production, and alterations in gene expression. a thorough understanding of these processes is indispensable for the development of heat tolerant crops. Key message we summarize recent studies focusing on the molecular basis of plant heat stress response (hsr), how hsr leads to thermotolerance, and promote plant adaptation to recurring heat stress events. abstract the global crop productivity is facing unprecedented threats due to climate change as high temperature negatively influences plant growth and metabolism. owing to their sessile.

Comments are closed.