Opioid Receptor вђ Artofit
Chapter 12 Opioids Drugs And Behavior The utilization of opioids in clinical pharmacology started after the extraction of morphine from the opium poppy papaver somniferum in 1806 with its use further intensified after the discovery of hypodermic needles in 1853.[1] opioids divide into two types, those being endogenous and exogenous. some endogenous opioids that bind to the receptors are enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins. The development of non addictive opioids depends on better understanding of opioid receptor structures and receptor signaling cascades. this review explains differences in pharmacological profiles and contextualizes recent developments in our understanding of the dynamic interactions between opioids, their receptors, and opioid receptor transducer coupling.
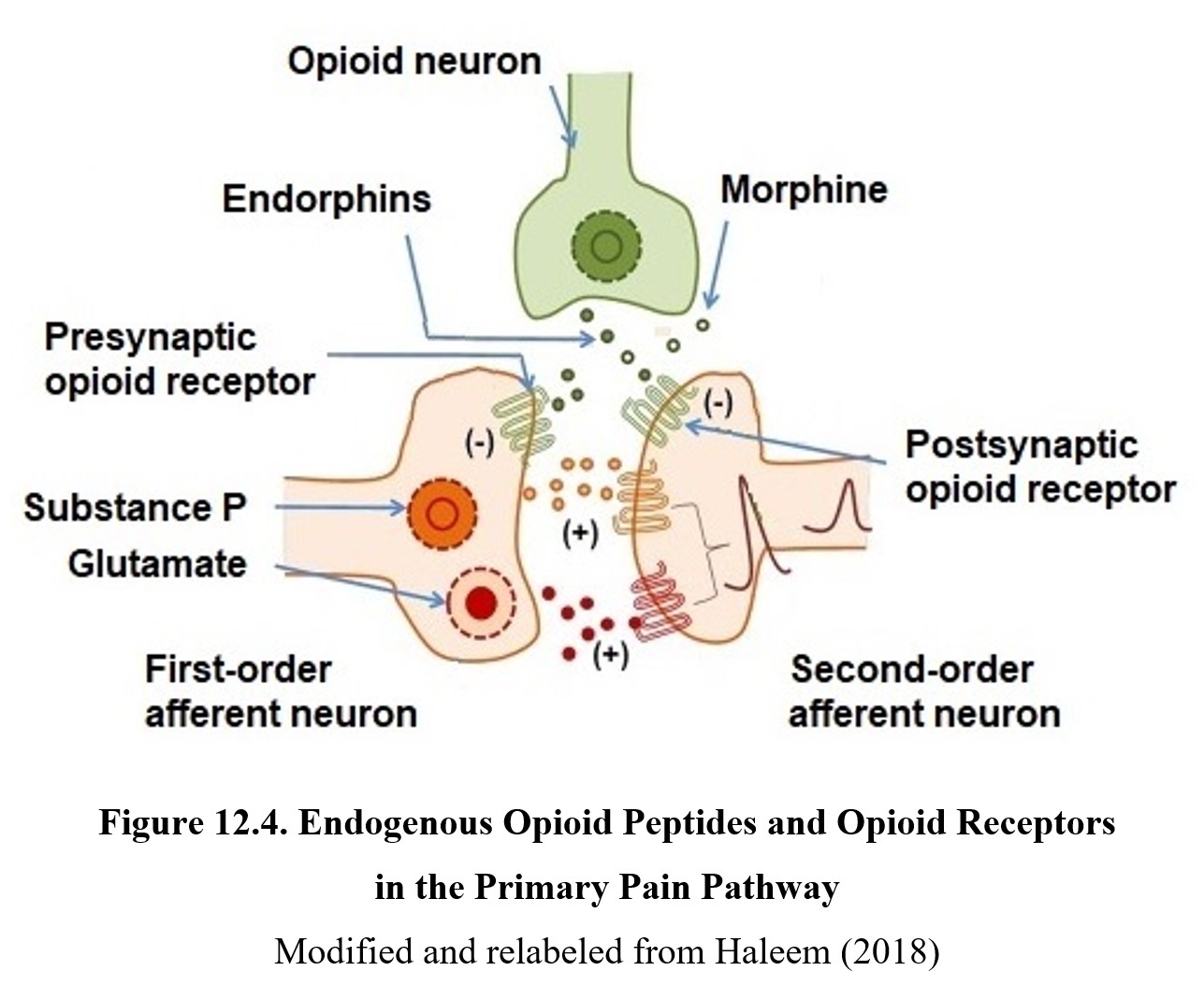
Opioid Mechanism Of Action Opioids Bind To Their вµ оє And оґ Receptors Download Scientific Opioid receptors were divided into three major types: μ (mu, mor), δ (delta, dor), and κ (kappa, kor) [2–4]. all three opioid receptor types were cloned in the 1990s, first dor from mice , followed by kor [6, 7] and mor . over the years opioid receptors were characterized at biochemical and pharmacological levels. The sf9 cells were cultured in esf 921 serum free medium (expression systems). for expression of opioid receptor g i signaling complexes, baculoviruses of each opioid receptor, g αi1, g β1, and g γ2 were added in equal proportions to the cell culture when the cell density reached 4×10 6 cells ml. The 1970’s heralded a new era in the opioid field with the discovery that opiate drugs produce their effects by binding to specific binding sites in brain, followed by the discovery that brain. Opioid receptors. opioid receptors are class a g protein coupled receptors (gpcrs) and are part of a family; these are the classical naloxone sensitive mop, δ (delta, dop) and kop along with the non classical receptor for nociceptin orphanin fq (n ofq) or nop (fig 1).16, 17, 18, 19 the consequences of receptor interactions will be discussed later.
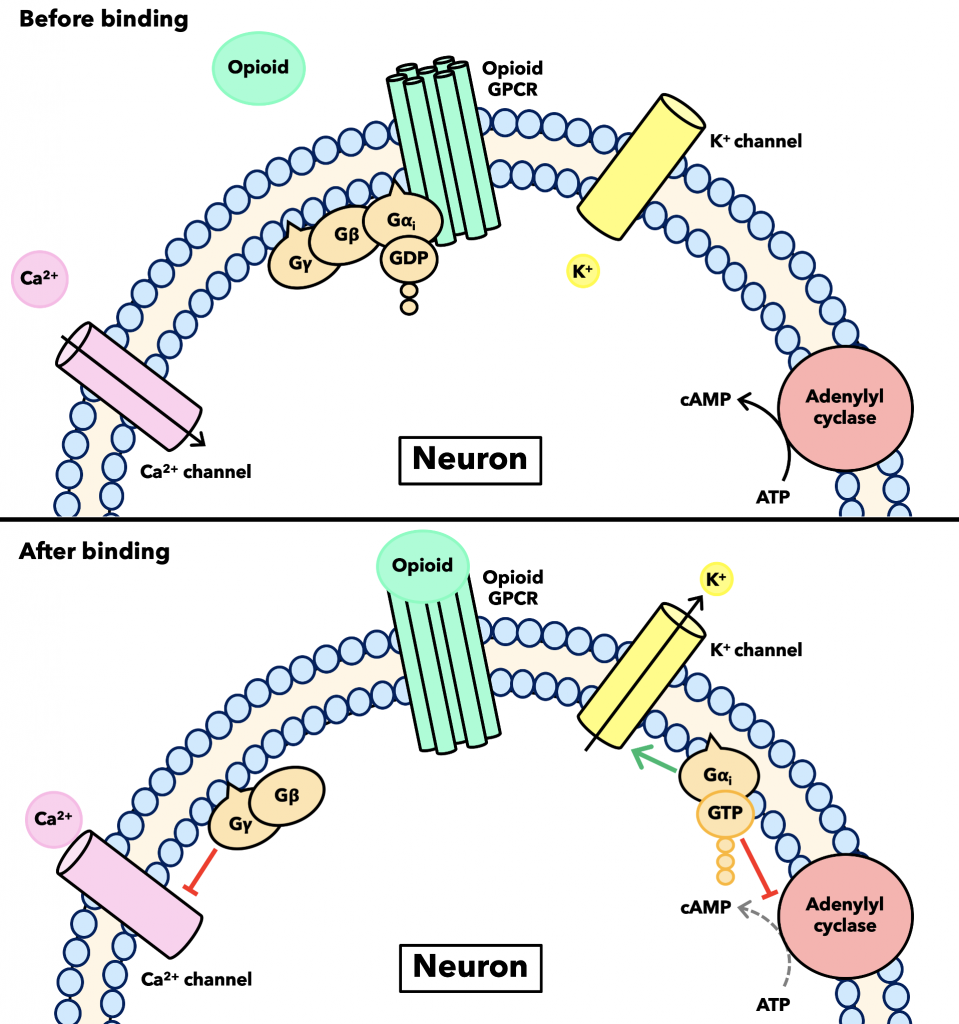
General Opioid Signaling вђ Opioid Peptides The 1970’s heralded a new era in the opioid field with the discovery that opiate drugs produce their effects by binding to specific binding sites in brain, followed by the discovery that brain. Opioid receptors. opioid receptors are class a g protein coupled receptors (gpcrs) and are part of a family; these are the classical naloxone sensitive mop, δ (delta, dop) and kop along with the non classical receptor for nociceptin orphanin fq (n ofq) or nop (fig 1).16, 17, 18, 19 the consequences of receptor interactions will be discussed later. The μ opioid receptor (μor) represents an important target of therapeutic and abused drugs. so far, most understanding of μor activity has focused on a subset of known signal transducers and. The μ opioid receptor (μor) is a g protein coupled receptor (gpcr) and the target of most clinically and recreationally used opioids. the induced positive effects of analgesia and euphoria are.

Comments are closed.