Factors Affecting Standard Reduction Potential Chemistry General Concepts

Factors Affecting Standard Reduction Potential Chemistry General Concepts Youtube Factors affecting standard reduction potential chemistry general conceptstemperaturepressureconcentration of the solution#srpfactors. Factors that influence reduction potential. in general, the ions of very late transition metals those towards the right hand end of the transition metal block, such as copper, silver and gold have high reduction potentials. in other words, their ions are easily reduced. alkali metal ions on the very left edge of the periodic table.
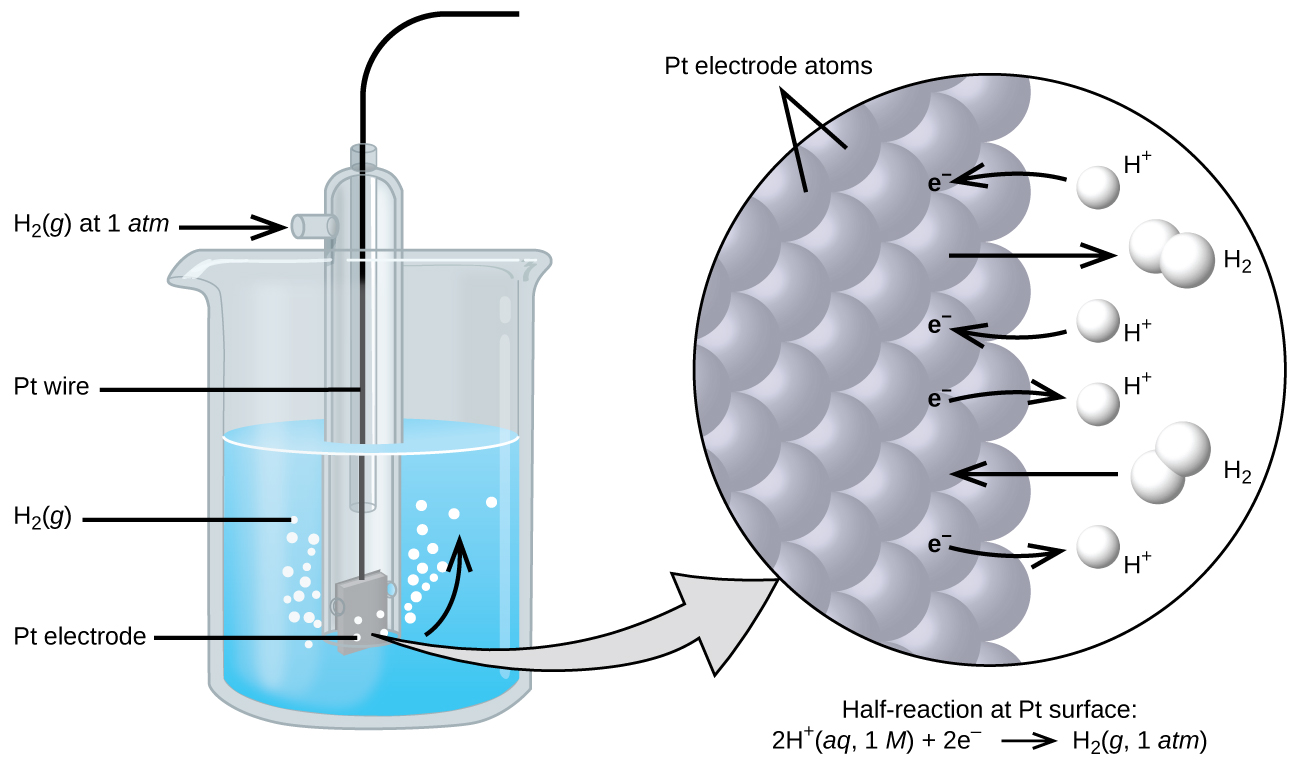
11 2 Standard Reduction Potential Chemistry Libretexts Glossary standard cell potential \( (e^\circ \ce{cell})\) the cell potential when all reactants and products are in their standard states (1 bar or 1 atm or gases; 1 m for solutes), usually at 298.15 k; can be calculated by subtracting the standard reduction potential for the half reaction at the anode from the standard reduction potential for the half reaction occurring at the cathode. The reduction half reaction chosen as the reference is. 2h (aq,1 m) 2e − ⇌ h2(g, 1 atm) e ∘ = 0 v. e ° is the standard reduction potential. the superscript “°” on the e denotes standard conditions (1 bar or 1 atm for gases, 1 m for solutes). the voltage is defined as zero for all temperatures. figure 1. It is important that the formula: Δe0r (cell) = eor (cathode) – eor (anode) is dissected and explained in details. · explain to students that in order to develop a reduction potentials table, a standard hydrogen half cell is assigned an electric potential of exactly 0 volts. define how hydrogen half cells are constructed. Use standard reduction potentials to determine the better oxidizing or reducing agent from among several possible choices. the cell potential in chapter 17.2 galvanic cells ( 0.46 v) results from the difference in the electrical potentials for each electrode. while it is impossible to determine the electrical potential of a single electrode, we.
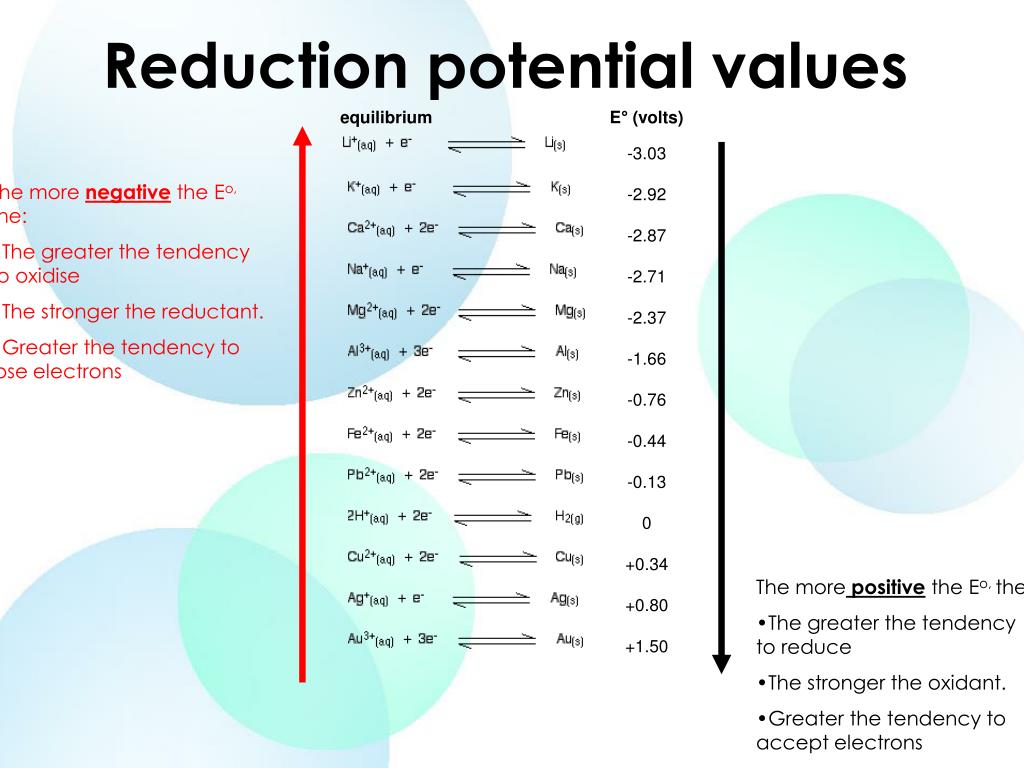
Ppt Standard Reduction Potential Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3000316 It is important that the formula: Δe0r (cell) = eor (cathode) – eor (anode) is dissected and explained in details. · explain to students that in order to develop a reduction potentials table, a standard hydrogen half cell is assigned an electric potential of exactly 0 volts. define how hydrogen half cells are constructed. Use standard reduction potentials to determine the better oxidizing or reducing agent from among several possible choices. the cell potential in chapter 17.2 galvanic cells ( 0.46 v) results from the difference in the electrical potentials for each electrode. while it is impossible to determine the electrical potential of a single electrode, we. Table 17.3.1 provides a listing of standard electrode potentials for a selection of half reactions in numerical order, and a more extensive listing is given in standard electrode (half cell) potentials. table 17.3.1. selected standard reduction potentials at 25 °c. half reaction. The reduction half reaction chosen as the reference is. 2h (aq,1m) 2e− ⇌ h2(g,1 atm) e∘ = 0 v 2 h (a q, 1 m) 2 e − ⇌ h 2 (g, 1 atm) e ∘ = 0 v. e ° is the standard reduction potential. the superscript “°” on the e denotes standard conditions (1 bar or 1 atm for gases, 1 m for solutes). the voltage is defined as zero for all.

Electrochemistry The Standard Reduction Potential Youtube Table 17.3.1 provides a listing of standard electrode potentials for a selection of half reactions in numerical order, and a more extensive listing is given in standard electrode (half cell) potentials. table 17.3.1. selected standard reduction potentials at 25 °c. half reaction. The reduction half reaction chosen as the reference is. 2h (aq,1m) 2e− ⇌ h2(g,1 atm) e∘ = 0 v 2 h (a q, 1 m) 2 e − ⇌ h 2 (g, 1 atm) e ∘ = 0 v. e ° is the standard reduction potential. the superscript “°” on the e denotes standard conditions (1 bar or 1 atm for gases, 1 m for solutes). the voltage is defined as zero for all.

Comments are closed.