Emphysema Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Centriacinar Panacinar Paraseptal

Emphysema Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Centriacinar Panacinar Paraseptal Youtube Paraseptal emphysema is the least common of the three main types of emphysema. the other forms of emphysema are centriacinar and panacinar. centriacinar tends to cause the most harm in the. Paraseptal emphysema (pse) is a type of pulmonary emphysema. individuals with both pse and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) panlobular (panacinar): affects all areas of the lungs.
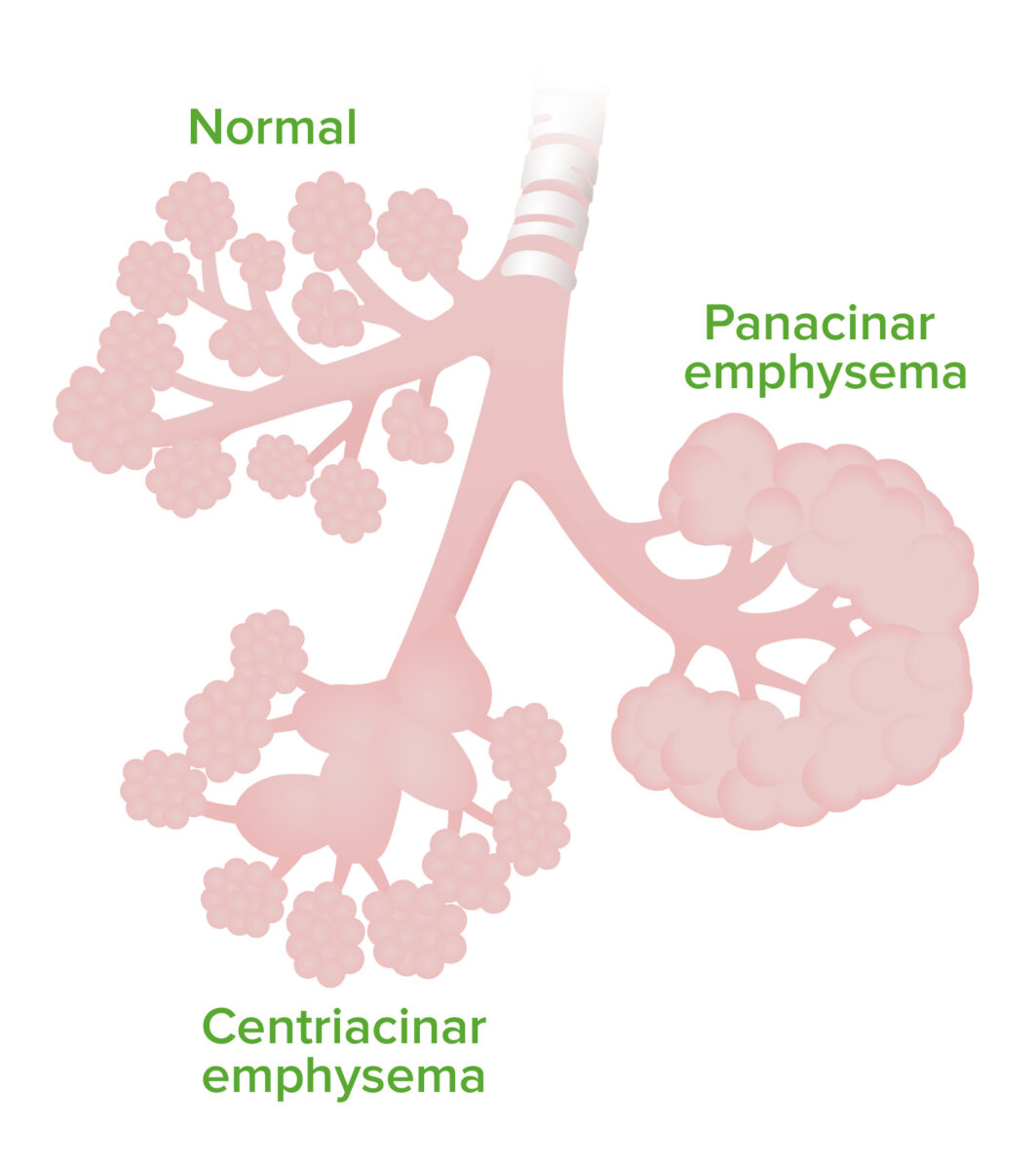
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Copd Concise Medical Knowledge Copd: a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms (dyspnea, cough, sputum production and or exacerbations) due to abnormalities of the airways (bronchitis, bronchiolitis) and or alveoli (emphysema) that cause permanent and often progressive airflow obstruction. (gold 2024). Prognosis. panlobular (or panacinar) emphysema is a type of emphysema that affects a specific part of the lungs. emphysema is a disease of the lungs in which the air sacs in the lungs (alveoli) are permanently damaged. there are three emphysema types—centriacinar, panlobular, and paraseptal—that affect different parts of the lung structure. Centrilobular emphysema, or centriacinar emphysema, is a long term, progressive lung disease. it’s considered to be a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). Pulmonary emphysema can be classified into three major subtypes based on the disease distribution within secondary pulmonary lobules (stern and frank 1994; thurlbeck and müller 1994): centriacinar emphysema, panacinar emphysema, and distal acinar emphysema (figure 8). the relationships among these types of pulmonary emphysema and how each type.

Emphysema Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Centriacinar Panacinar Paraseptal Youtube Centrilobular emphysema, or centriacinar emphysema, is a long term, progressive lung disease. it’s considered to be a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). Pulmonary emphysema can be classified into three major subtypes based on the disease distribution within secondary pulmonary lobules (stern and frank 1994; thurlbeck and müller 1994): centriacinar emphysema, panacinar emphysema, and distal acinar emphysema (figure 8). the relationships among these types of pulmonary emphysema and how each type. Outlook. centrilobular emphysema is a form of chronic lung disease. this form of emphysema affects the upper lobes of the lungs and is common in people who smoke. centrilobular emphysema is also. Pulmonary emphysema, a progressive lung disease, is a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). emphysema is primarily a pathological diagnosis that affects the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchiole. it is characterized by abnormal permanent enlargement of lung air spaces with the destruction of their walls (septa of alveoli.

Emphysema Causes Signs Symptoms Stages Expectancy Treatment Outlook. centrilobular emphysema is a form of chronic lung disease. this form of emphysema affects the upper lobes of the lungs and is common in people who smoke. centrilobular emphysema is also. Pulmonary emphysema, a progressive lung disease, is a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). emphysema is primarily a pathological diagnosis that affects the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchiole. it is characterized by abnormal permanent enlargement of lung air spaces with the destruction of their walls (septa of alveoli.

Comments are closed.