What Is Secondary Consumers

Secondary Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary A secondary consumer is an organism that eats primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are herbivores that only eat plants. secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores and are important for the food chain and energy flow. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores.

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy. Secondary consumers occupy the third trophic level in a typical food chain. they are organisms that feed on primary consumers for nutrients and energy. while primary consumers are always herbivores; organisms that only feed on autotrophic plants, secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores eat only animals, but omnivores eat. Secondary consumers are those that predate upon primary consumers, and tertiary consumers predate upon secondary consumers. secondary consumers are either carnivores (which eat meat) or omnivores. Secondary consumers often exhibit specialized physical features that aid in hunting. for example, raptors like hawks and eagles possess sharp talons and beaks designed to tear flesh, while felines such as tigers and leopards have powerful limbs and retractable claws for taking down prey.
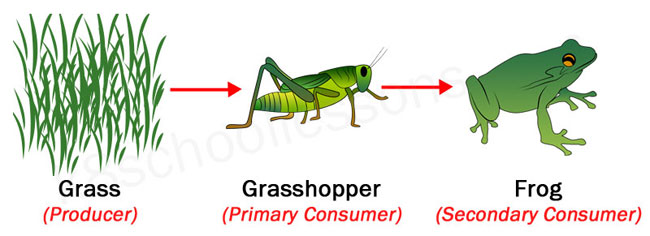
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs Secondary consumers are those that predate upon primary consumers, and tertiary consumers predate upon secondary consumers. secondary consumers are either carnivores (which eat meat) or omnivores. Secondary consumers often exhibit specialized physical features that aid in hunting. for example, raptors like hawks and eagles possess sharp talons and beaks designed to tear flesh, while felines such as tigers and leopards have powerful limbs and retractable claws for taking down prey. Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, which are plants or herbivores. they are either carnivores or omnivores, and they play a role in controlling the population of primary consumers and providing energy to tertiary consumers. Secondary consumer. definition noun, plural: secondary consumers any organism that consumes or feeds largely on primary consumers, as well as autotrophs supplement a food chain is a feeding hierarchy showing the various trophic levels. a trophic level is a position in a food chain or an ecological pyramid.
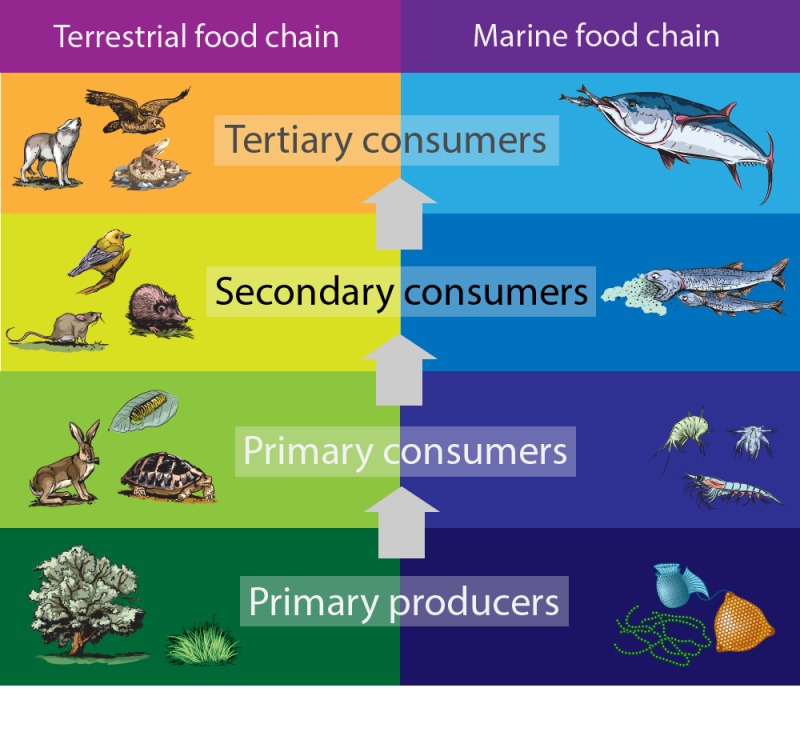
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, which are plants or herbivores. they are either carnivores or omnivores, and they play a role in controlling the population of primary consumers and providing energy to tertiary consumers. Secondary consumer. definition noun, plural: secondary consumers any organism that consumes or feeds largely on primary consumers, as well as autotrophs supplement a food chain is a feeding hierarchy showing the various trophic levels. a trophic level is a position in a food chain or an ecological pyramid.
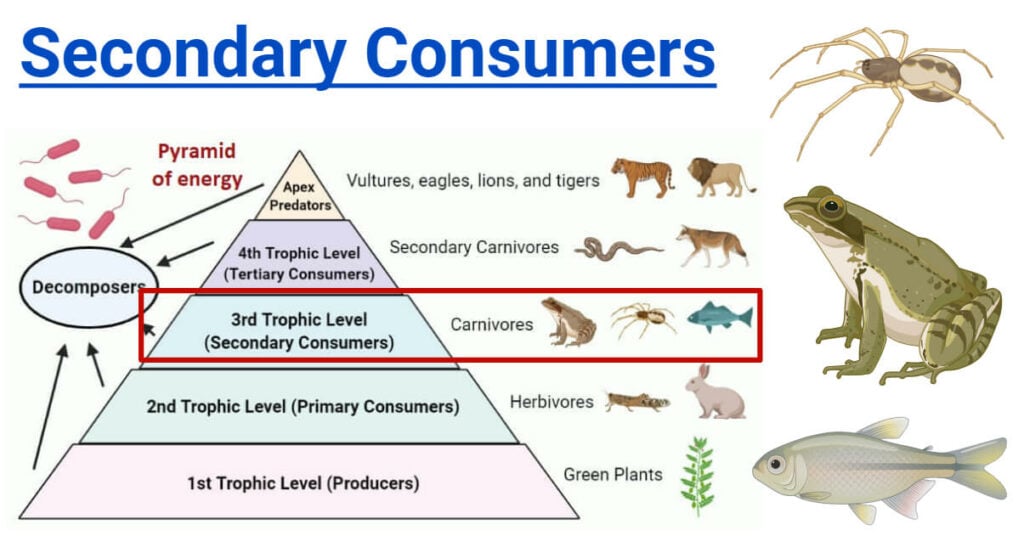
Secondary Consumers Types Food Chain Examples Roles

Comments are closed.