What Eats Primary And Secondary Consumers
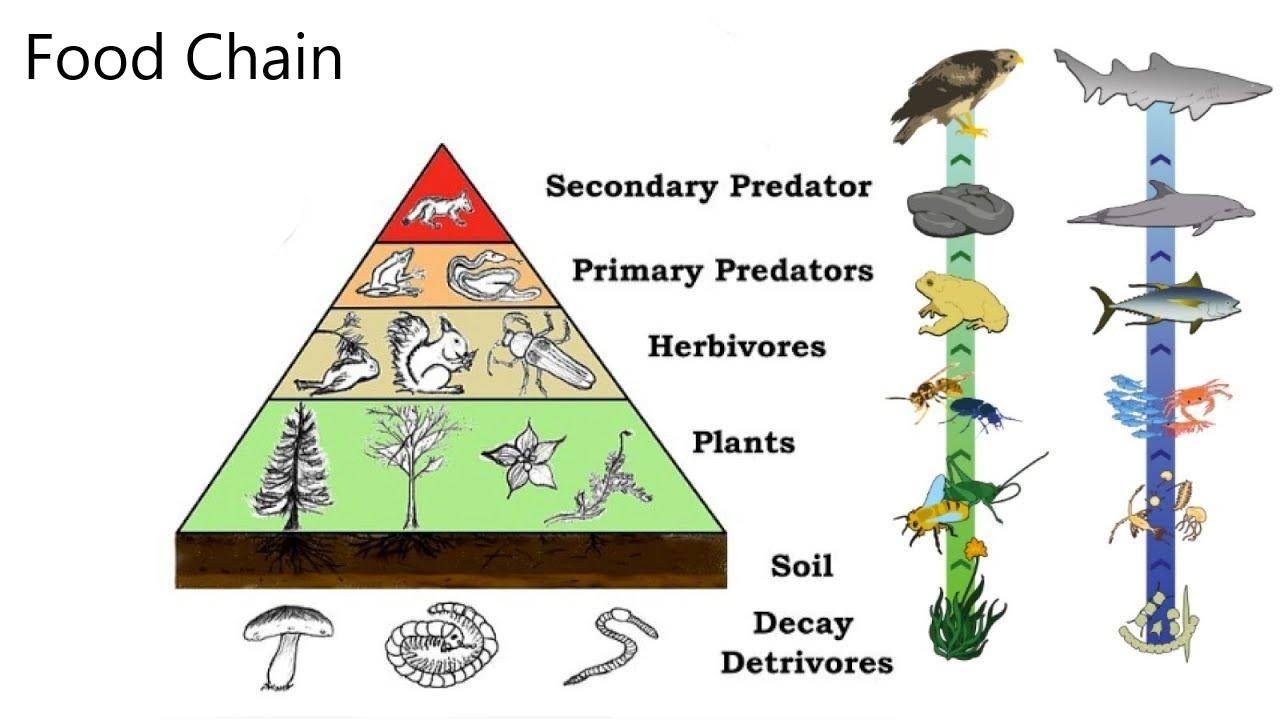
This Is A Food Web Showing Primary Secondary And Tert Vrogue Co Secondary consumer definition. secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are always herbivores, or organisms that only eat autotrophic plants. however, secondary consumers can either be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores only eat other animals, and omnivores eat both plant and animal matter. These are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the herbivores. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers.

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Food Chain The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores: the primary consumers. secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores. A consumer is a living thing that eats other plants and animals. the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer. the next one is the secondary consumer. There are certain primary consumers that are called specialists because they only eat one type of producers. an example is the koala, because it feeds only on eucalyptus leaves. primary consumers that feed on many kinds of plants are called generalists. secondary consumers are small medium sized carnivores that prey on herbivorous animals.

3 12 12 A consumer is a living thing that eats other plants and animals. the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer. the next one is the secondary consumer. There are certain primary consumers that are called specialists because they only eat one type of producers. an example is the koala, because it feeds only on eucalyptus leaves. primary consumers that feed on many kinds of plants are called generalists. secondary consumers are small medium sized carnivores that prey on herbivorous animals. For example, a grasshopper living in the everglades is a primary consumer. some other examples of primary consumers are white tailed deer that forage on prairie grasses, and zooplankton that eat microscopic algae in the water. next are the secondary consumers, which eat primary consumers. secondary consumers are mostly carnivores, from the. These small herbivores eat dozens of kilograms (pounds) of giant kelp every day. secondary consumers eat herbivores. they are at the third trophic level. in a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. in the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. tertiary consumers eat the secondary.
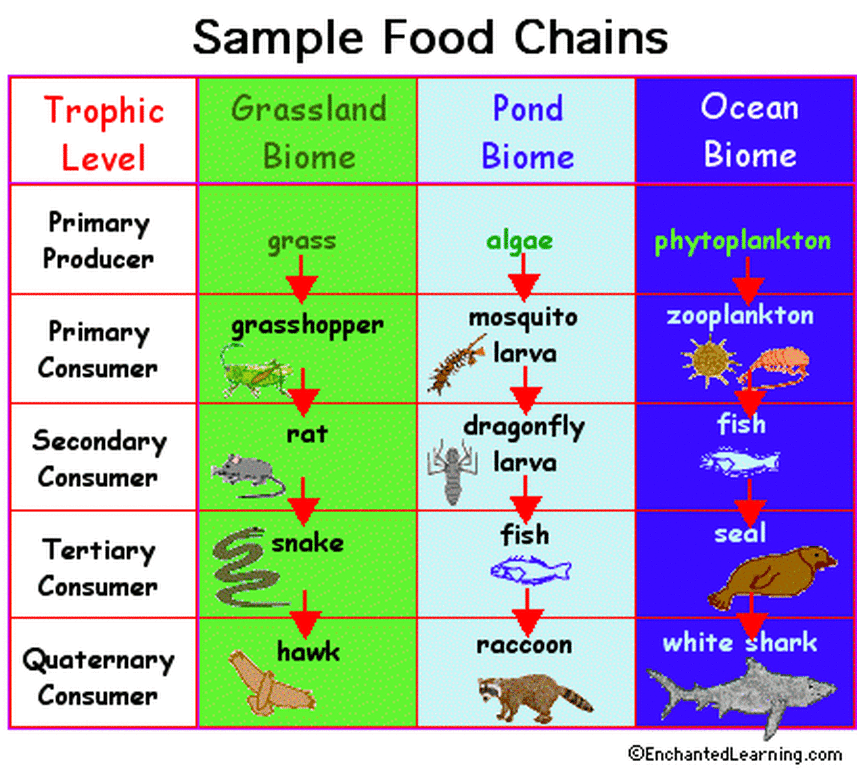
Food Chain And Web Ecology For example, a grasshopper living in the everglades is a primary consumer. some other examples of primary consumers are white tailed deer that forage on prairie grasses, and zooplankton that eat microscopic algae in the water. next are the secondary consumers, which eat primary consumers. secondary consumers are mostly carnivores, from the. These small herbivores eat dozens of kilograms (pounds) of giant kelp every day. secondary consumers eat herbivores. they are at the third trophic level. in a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. in the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. tertiary consumers eat the secondary.

Comments are closed.