Trophic Food Web Webs Concepts Ecological Web Decomposers Trophic Levels Consumers
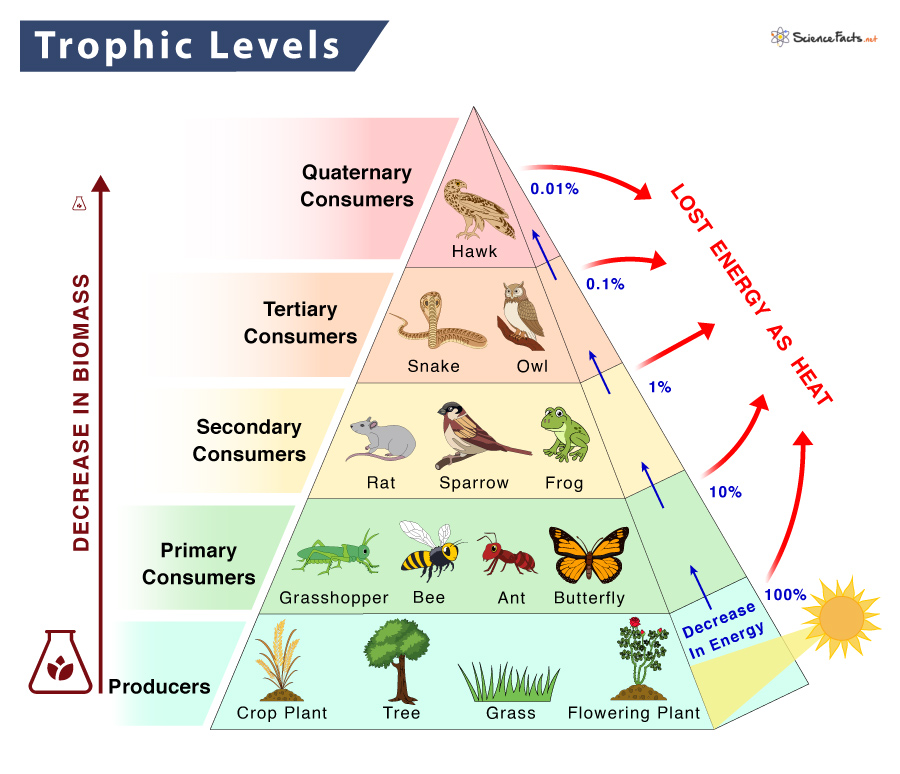
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram Food web is an important ecological concept. basically, food web represents feeding relationships within a community (smith and smith 2009). the second consumers (trophic level 3) in the. Further trophic levels are numbered subsequently according to how far the organism is along the food chain. level 1: plants and algae make their own food and are called producers. level 2: herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers. level 3: carnivores that eat herbivores are called secondary consumers.
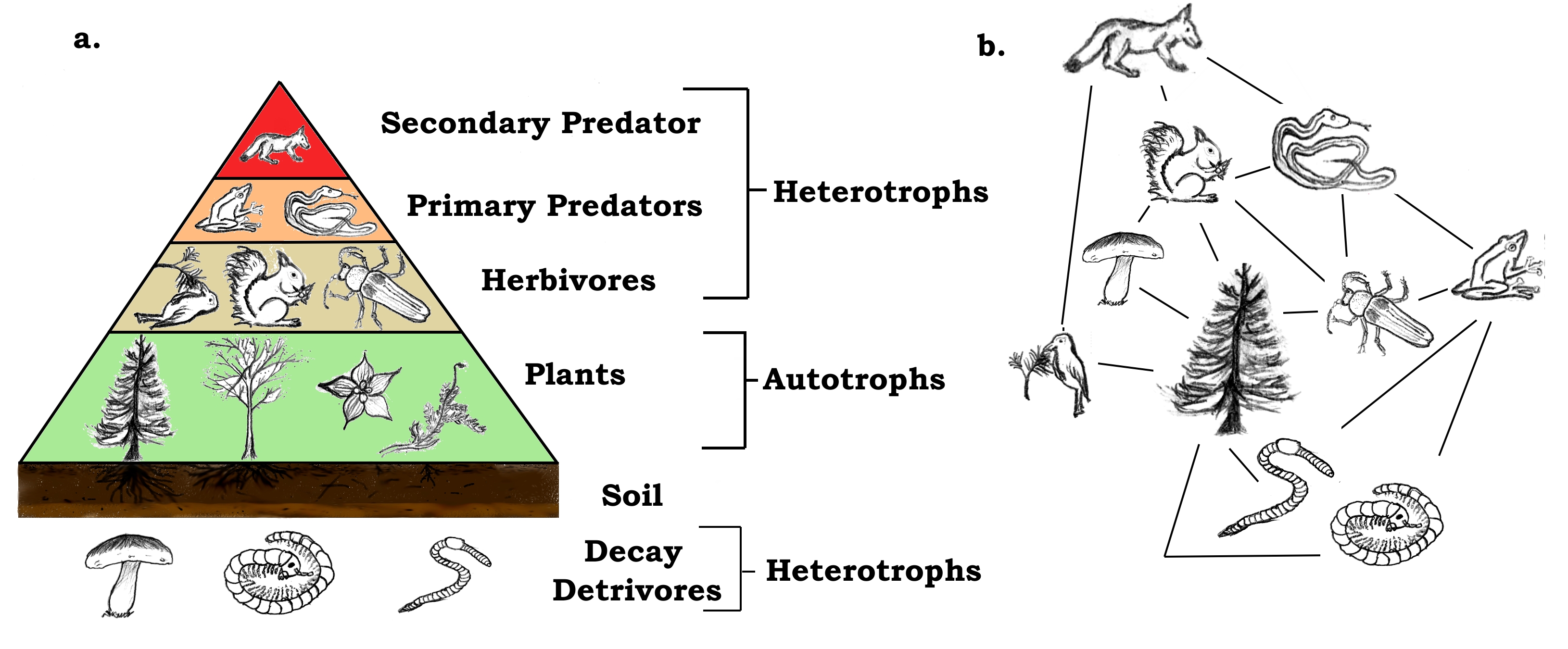
Ecological Concepts Food Webs All of the interconnected and overlapping food chains in an ecosystem make up a food web. trophic levels organisms in food webs are grouped into categories called trophic levels. roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers, and decomposers (last trophic level). Energy flow food webs. energy flow food webs depict the relationship between organisms by measuring and showing the energy flux between organisms. 4. fossil food webs. in fossil food webs, the relationship between organisms is established based on fossil records. 5. functional food webs. The concept of the trophic level was one of the first concepts to be introduced in ecology that provides a better understanding of energy flow and control within food webs. the concept was introduced by raymond lindeman in 1942 based on the studies of august thienemann who also coined the terms ‘producer’, ‘consumers’, and ‘reducers’. A food web is a concept that accounts for the multiple trophic (feeding) interactions between each species and the many species it may feed on, or that feed on it. in a food web, the several trophic connections between each species and the other species that interact with it may cross multiple trophic levels.
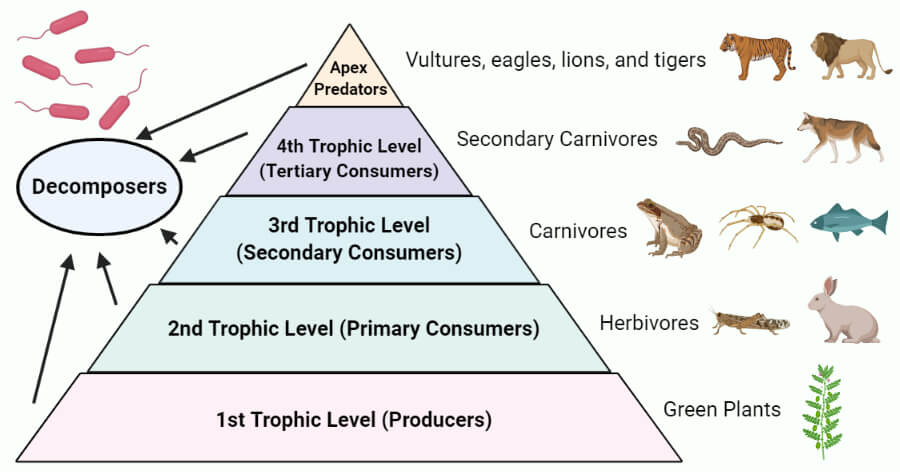
Trophic Level Food Chain Food Web Pyramid Examples The concept of the trophic level was one of the first concepts to be introduced in ecology that provides a better understanding of energy flow and control within food webs. the concept was introduced by raymond lindeman in 1942 based on the studies of august thienemann who also coined the terms ‘producer’, ‘consumers’, and ‘reducers’. A food web is a concept that accounts for the multiple trophic (feeding) interactions between each species and the many species it may feed on, or that feed on it. in a food web, the several trophic connections between each species and the other species that interact with it may cross multiple trophic levels. Food chain: determine the linear flow of energy and nutrients from one trophic level to the next. food web: learn about the relationships between creatures and the complexities of trophic interactions. ecological pyramids: examine the distribution of population, biomass, and energy at various trophic levels, and consider the implications for. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.
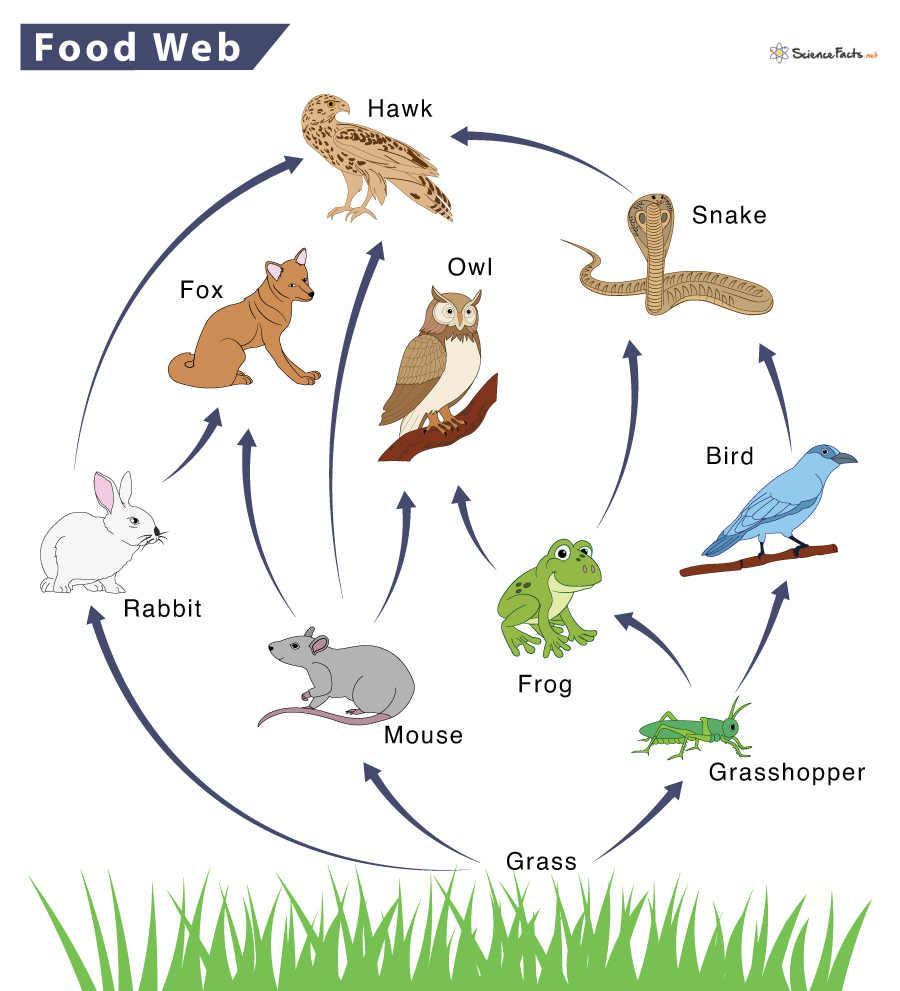
Food Web вђ Definition Trophic Levels Types And Example Food chain: determine the linear flow of energy and nutrients from one trophic level to the next. food web: learn about the relationships between creatures and the complexities of trophic interactions. ecological pyramids: examine the distribution of population, biomass, and energy at various trophic levels, and consider the implications for. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.

Comments are closed.