Solved Hemolysis Of Blood Agar Plates 21 Identify The Type Chegg
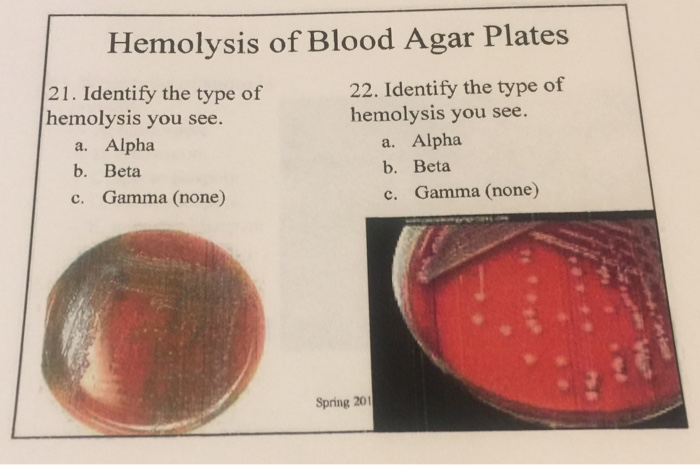
Solved Hemolysis Of Blood Agar Plates 21 Identify The Type Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: hemolysis of blood agar plates 21. identify the type of hemolysis you see. a. alpha 22. identify the type of hemolysis you see. a. alpha b. beta b. beta c. gamma (none) c. gamma (none spring 20. there are 3 steps to solve this one. Question: this type of hemolysis on blood agar plates produces clearing of the red blood cells that surround the colony.gammabetalambdaalpha. this type of hemolysis on blood agar plates produces clearing of the red blood cells that surround the colony. here’s the best way to solve it. beta hemolysis produces a clear zone around the co.
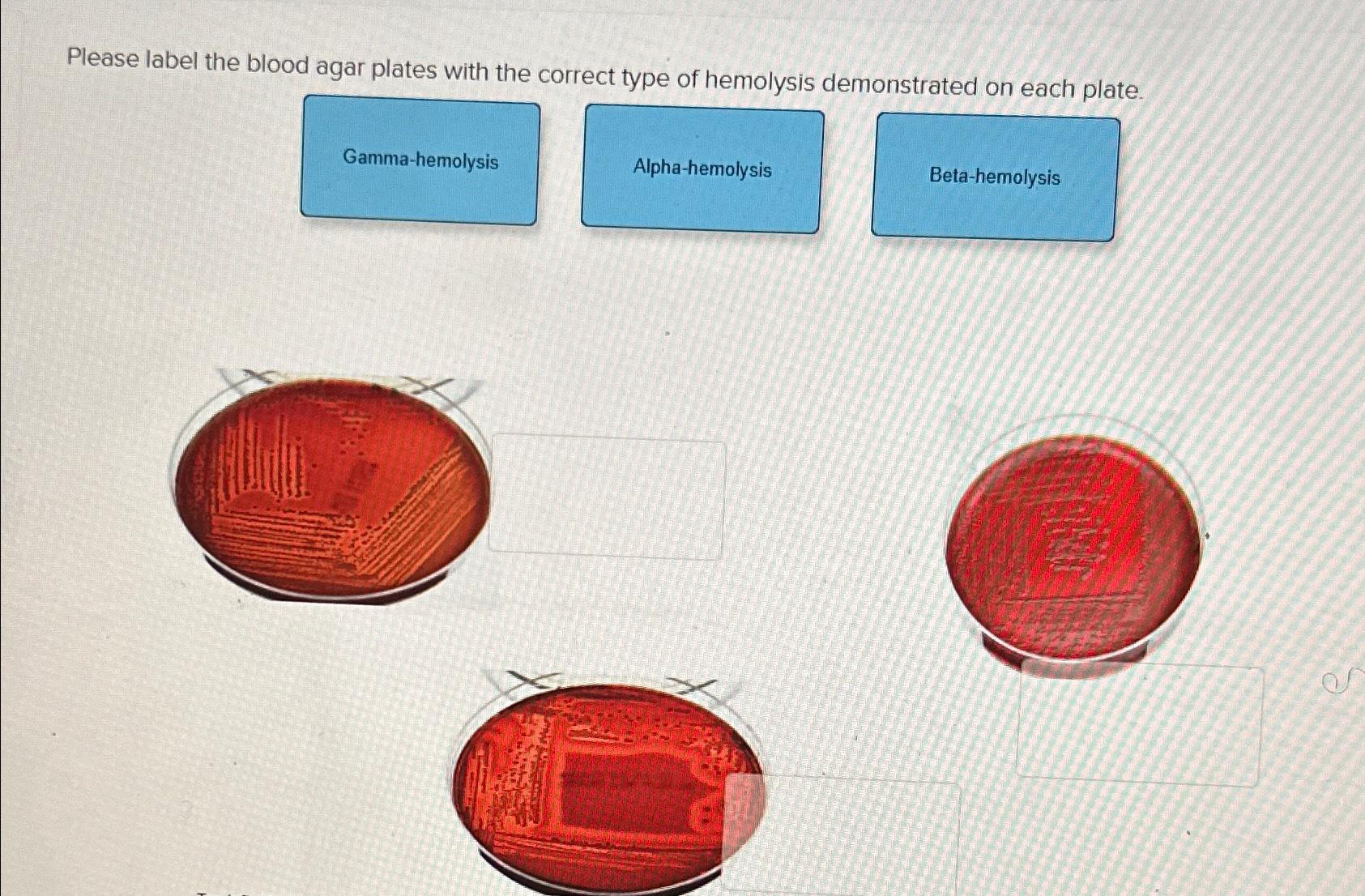
Solved Please Label The Blood Agar Plates With The Correct Chegg Alpha hemolysis and example. partial destruction of red blood cells, greenish gray. zone of the blood surrounding the colony. streptococcus pneumoniae. beta hemolysis and example. complete destruction of the red blood cells forming a zone of clearing around the. colony. streptococcus pyogenes. staphylococcus aureus. Blood agar consists of a base containing a protein source (e.g. tryptones), soybean protein digest, sodium chloride (nacl), agar, and 5% sheep blood blood contains inhibitors for certain bacteria such as neisseria and haemophilus genera, so the blood agar must be heated to inactivate these inhibitors and to release essential growth factors (e.g., v factor). Complete destruction of red blood cells. on a blood agar plate, alpha hemolysis usually results in a darkening of the agar surrounding the bacterial growth and a greenish tint to the media. the green tint found in the media. is due to the oxidation of iron from hemoglobin left behind after hemolysis. beta homolytic streptococci are classified. To prepare the medium, the tsa is cooled, the blood is added aseptically, and then the plates are poured. (1) there are two types of hemolysis. alpha hemolysis (α) is caused by damage (but not lysis) of the rbcs in the blood; the media is translucent with a green ish tinge around the colonies (1). beta hemolysis (β) is lysis of the rbcs and.

Comments are closed.