Secondary Consumers Heterotrophs Omnivores Education Notes Youtube

Secondary Consumers Heterotrophs Omnivores Education Notes Youtube # secondary consumer # heterotrophs #food chain # trophic level animals that depends on producers as well as primary consumers.they can be both omnivores and. Learn all about the different types of heterotrophs. these include carnivores, herbivores, omnivores, and decomposers. each of these organisms has to get the.
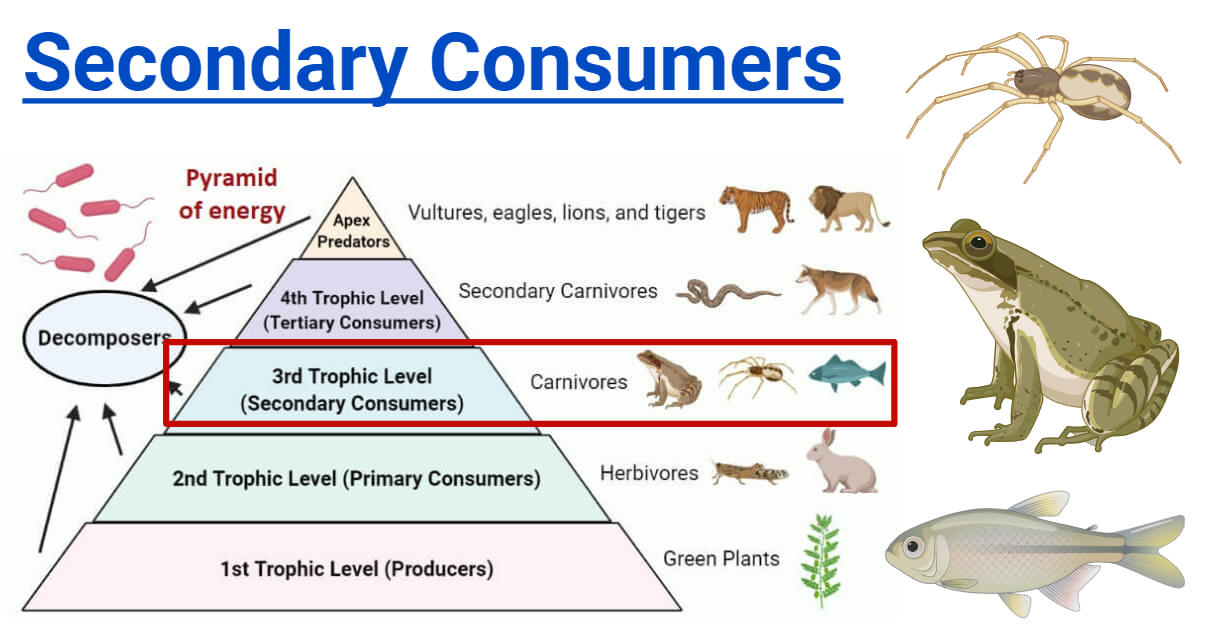
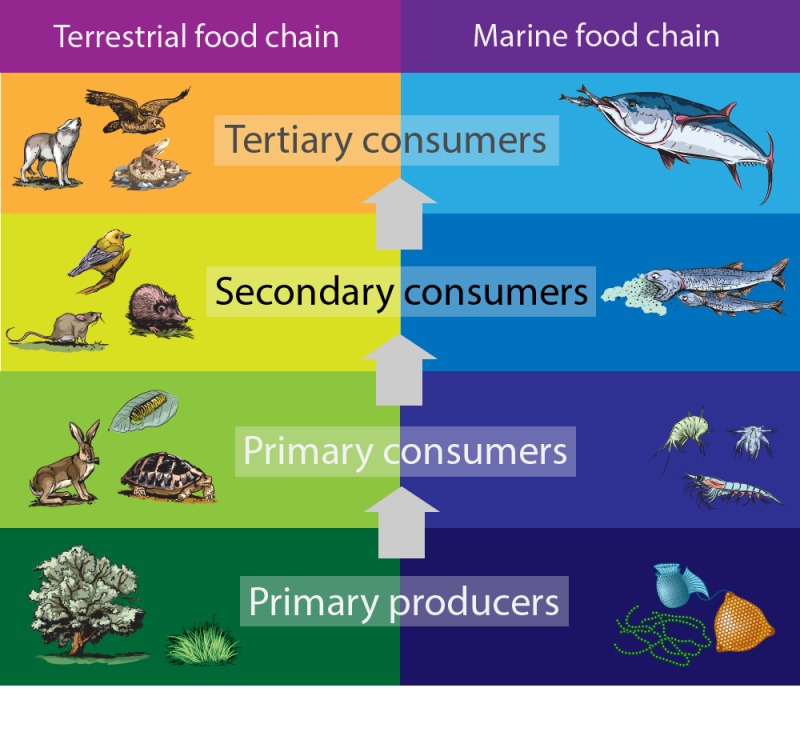
Secondary Consumers Types Food Chain Examples Roles Learn more about heterotrophs moomoomath types of heterotrophs with examples heterotrophs get their energy from eating other plants, animal. Secondary consumer definition. secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are always herbivores, or organisms that only eat autotrophic plants. however, secondary consumers can either be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores only eat other animals, and omnivores eat both plant and animal matter. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores. Noun. aquatic animal that strains nutrients from water. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle.

Consumer Biology Britannica Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores. Noun. aquatic animal that strains nutrients from water. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. Heterotrophs are primarily classified into four different types based on their food habit and presence in the food chain. they are herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and detritivores. 1. herbivores feed on autotrophs like plants and algae for food. herbivores occupy the second trophic level of the food chain. examples: deer, cow, and buffalo. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores, from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals. ecosystems can also have tertiary consumers.
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples Heterotrophs are primarily classified into four different types based on their food habit and presence in the food chain. they are herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and detritivores. 1. herbivores feed on autotrophs like plants and algae for food. herbivores occupy the second trophic level of the food chain. examples: deer, cow, and buffalo. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores, from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals. ecosystems can also have tertiary consumers.

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Food Chain

Comments are closed.