Parts Of A Circle Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Vrogue Co
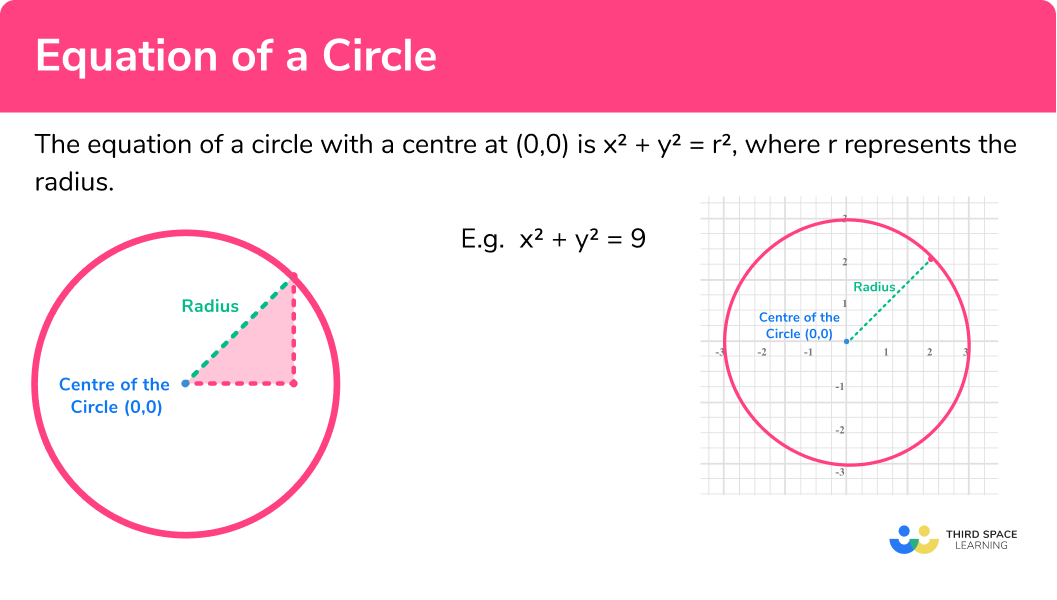
Parts Of A Circle Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Vrogue Co The parts of a circle are the radius, diameter, circumference, arc, chord, secant, tangent, sector and segment. circle terms. naming circle part s: circle. a round plane figure whose boundary consists of points equidistant from a fixed point. centre. Radius, sector, arc, tangent, chord, radii, diameter, circumference. practice questions. previous: arc length practice questions.
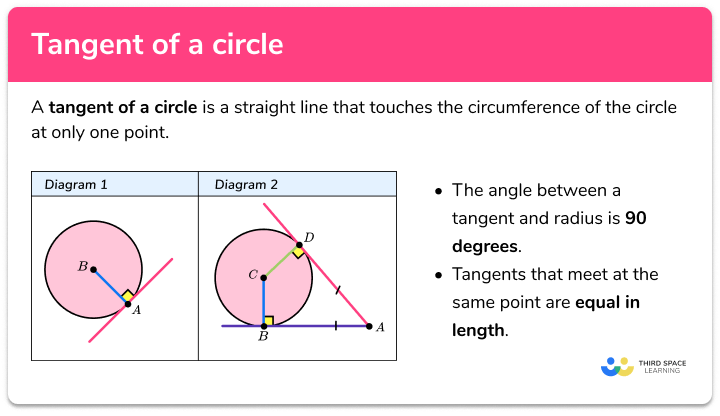
Parts Of A Circle Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Vrogue Co Example 1: the alternate segment theorem. the triangle abc is inscribed in a circle with centre o. the tangent de meets the circle at the point a. calculate the size of the angle abc. locate the key parts of the circle for the theorem. here we have: the tangent de. Parts of a circle diagram. radius a straight line from the center of the circle to the edge. diameter a straight line from one side of the circle to the other, going through the center of the circle. circumference the outside of the whole circle (the perimeter of the circle). tangent a line outside the circle which touches the circle at. On a related note, the second circle theorem we’re going to use is: opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral sum to 180. angle bae (which we just worked out) is opposite to angle cde, so \text{angle cde } = 180 121 = 59\degree . then, the final step to finding angle eda will be subtracting the size of angle cda from that of angle cde to get. Browse all circle resources. an extract from the revision sheet provides descriptions of the eight parts of a circle: the circumference. the distance once around the circle. an arc. part of the circumference. a chord. a line segment that goes from one point to another on the circle's circumference. a diameter.
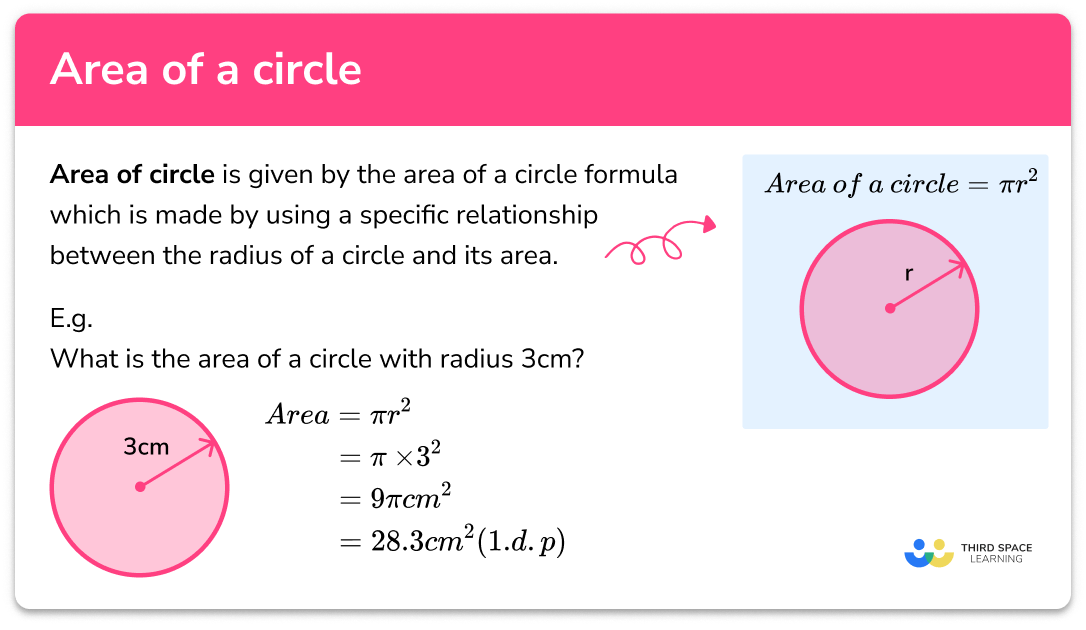
Parts Of A Circle Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Vrogue Co On a related note, the second circle theorem we’re going to use is: opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral sum to 180. angle bae (which we just worked out) is opposite to angle cde, so \text{angle cde } = 180 121 = 59\degree . then, the final step to finding angle eda will be subtracting the size of angle cda from that of angle cde to get. Browse all circle resources. an extract from the revision sheet provides descriptions of the eight parts of a circle: the circumference. the distance once around the circle. an arc. part of the circumference. a chord. a line segment that goes from one point to another on the circle's circumference. a diameter. Step #2: utilize angle information. given that angles in the same segment are equal, angle ade is equal to angle abc, so angle abc = 71°. additionally, because the perpendicular from the center of a circle to a chord bisects the chord, line be is equal to line ae, which means be = 5 cm. step #3: apply trigonometry. Remember to state the units of your answers. question 2: calculate the area of the circle below with a radius of 5 cm, giving your answers in terms of \pi. [2 marks] question 3: below is a circle with centre c and radius x\text { cm}. the area of this circle is 200\text { cm}^2. find the value of x to 1 dp.
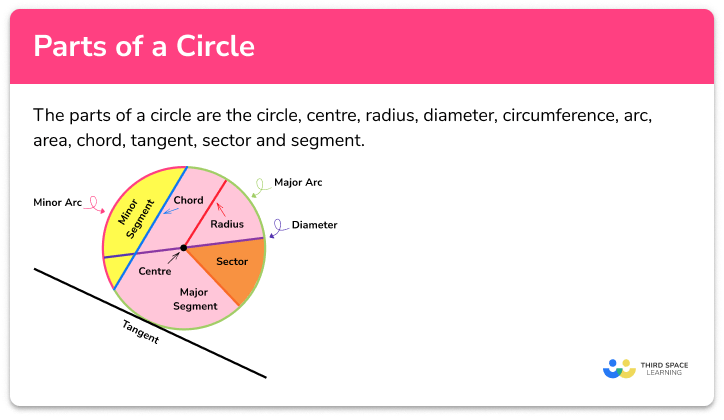
Parts Of A Circle Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Step #2: utilize angle information. given that angles in the same segment are equal, angle ade is equal to angle abc, so angle abc = 71°. additionally, because the perpendicular from the center of a circle to a chord bisects the chord, line be is equal to line ae, which means be = 5 cm. step #3: apply trigonometry. Remember to state the units of your answers. question 2: calculate the area of the circle below with a radius of 5 cm, giving your answers in terms of \pi. [2 marks] question 3: below is a circle with centre c and radius x\text { cm}. the area of this circle is 200\text { cm}^2. find the value of x to 1 dp.

Comments are closed.