Matrix Scalar Multiplication Properties Formula Examples

Matrix Scalar Multiplication Properties Formula Examples Properties of matrix scalar multiplication. if a and b are matrices of the same order; and k, a, and b are scalars then: a and ka have the same order. for example, if a is a matrix of order 2 x 3 then any of its scalar multiple, say 2a, is also of order 2 x 3. matrix scalar multiplication is commutative. i.e., k a = a k. K(a b) = ka kb (scalar multiplication distributive property) ka = ak. a 0 = 0 a = a (additive identity) 0a = 0. be sure that this last property makes sense; it says that if we multiply any matrix by the number 0, the result is the zero matrix, or 0. we began this section with the concept of matrix equality.
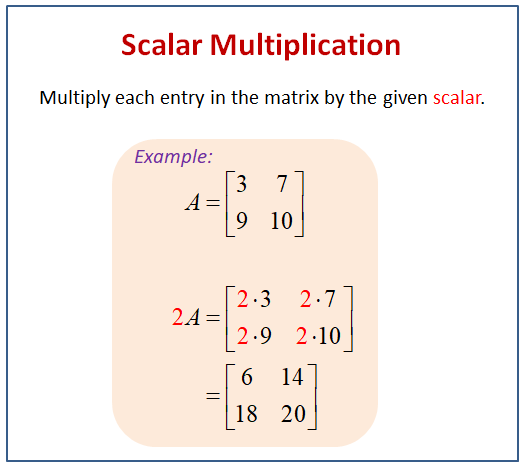
Scalar Multiplication Of Matrices Examples Solutions Videos Worksheets Activ When we work with matrices, we refer to real numbers as scalars. the term scalar multiplication refers to the product of a real number and a matrix. in scalar multiplication, each entry in the matrix is multiplied by the given scalar. for example, given that, a = [10 4 6 3] let’s find 2a. 2a = 2. [10 4 6 3]. Here’s the simple procedure as shown by the formula above. take the number outside the matrix (known as the scalar) and multiply it by each and every entry or element of the matrix. : given the following matrices, perform the indicated operation. apply. i will take the scalar 2 (similar to the coefficient of a term) and distribute it by. The properties of matrices can be broadly classified into the following five properties. properties of matrix addition. properties of scalar multiplication of matrix. properties of matrix multiplication. properties of transpose matrix. properties of inverse matrix and other properties. It is a special matrix, because when we multiply by it, the original is unchanged: a × i = a. i × a = a. order of multiplication. in arithmetic we are used to: 3 × 5 = 5 × 3 (the commutative law of multiplication) but this is not generally true for matrices (matrix multiplication is not commutative): ab ≠ ba.

Comments are closed.