How To Explain Homeostasis
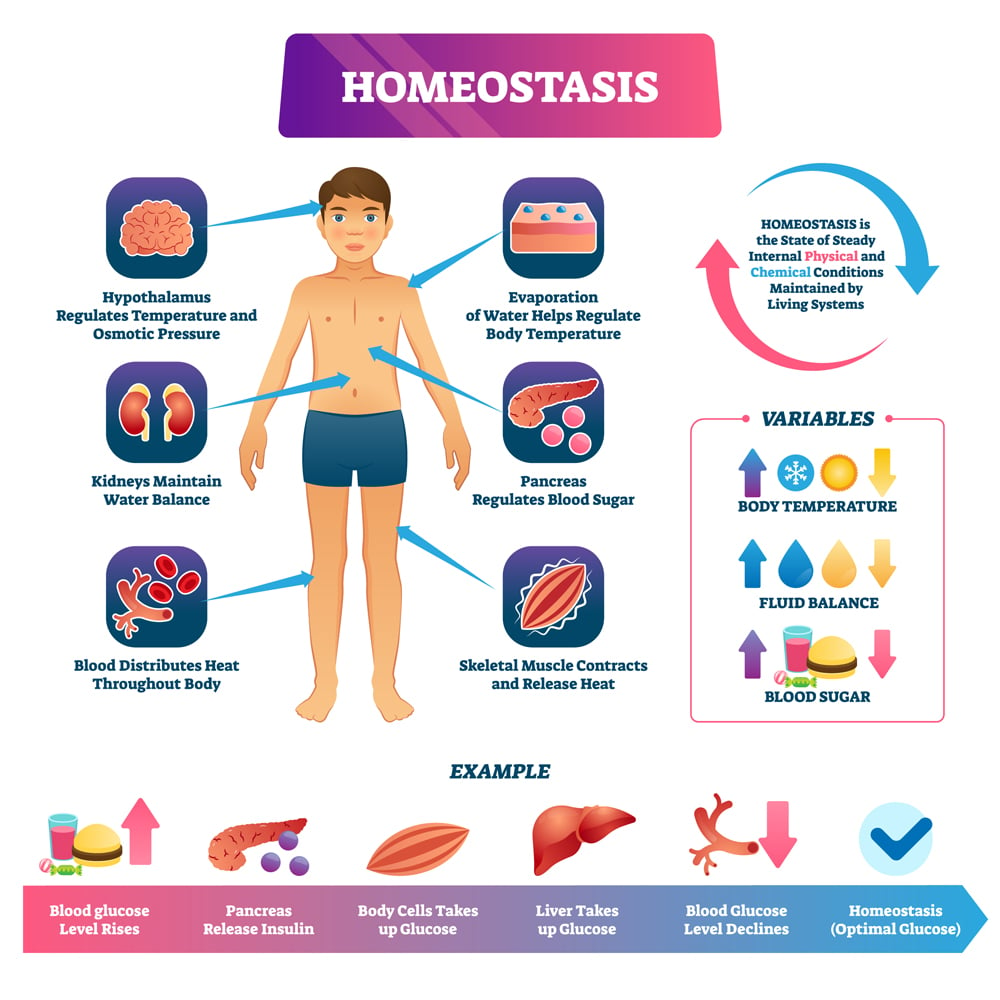
How To Explain Homeostasis Homeostasis, any self regulating process by which biological systems tend to maintain stability while adjusting to conditions that are optimal for survival. if homeostasis is successful, life continues; if unsuccessful, disaster or death ensues. the stability attained is actually a dynamic equilibrium, in which continuous change occurs yet. Homeostasis is the self regulation of processes in the body that maintains equilibrium of temperature, blood sugar, and much more. learn how receptors, control center, and effectors work together to adjust to changing conditions, and see examples of homeostasis in humans and other organisms.

How To Explain Homeostasis Homeostasis is a physiological process that keeps the internal environment of a living organism stable and balanced. learn how homeostasis works via negative feedback loops, what are the types of homeostasis, and why it is essential for survival. Homeostasis is an organism’s process of maintaining a stable internal environment suitable for sustaining life. learn how homeostasis regulates water, temperature, chemical levels, and more with examples and quizzes. Biology. homeostasis, from the greek words for "same" and "steady," refers to any process that living things use to actively maintain fairly stable conditions necessary for survival. the term was. In biology, homeostasis (british also homoeostasis; h ɒ m i oʊ ˈ s t eɪ s ɪ s, m i ə ) is the state of steady internal physical and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. [1] this is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance , being kept.
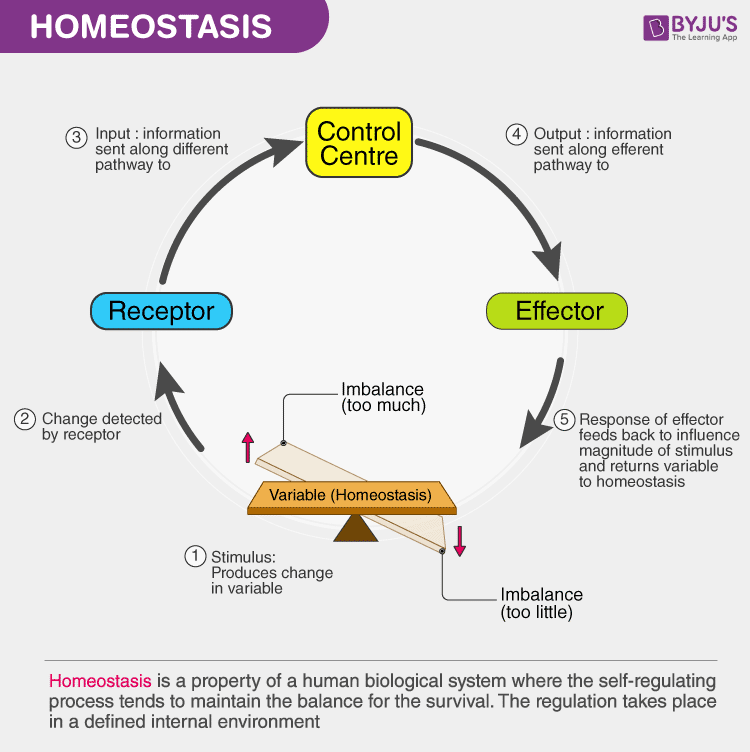
How To Explain Homeostasis Biology. homeostasis, from the greek words for "same" and "steady," refers to any process that living things use to actively maintain fairly stable conditions necessary for survival. the term was. In biology, homeostasis (british also homoeostasis; h ɒ m i oʊ ˈ s t eɪ s ɪ s, m i ə ) is the state of steady internal physical and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. [1] this is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance , being kept. An information hypothesis. homeostasis is the ability to maintain a relatively stable internal state that persists despite changes in the world outside. all living organisms, from plants to. Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment by negative or positive feedback mechanisms. learn how sensors, control centers and effectors regulate body parameters such as temperature, blood pressure and glucose levels.
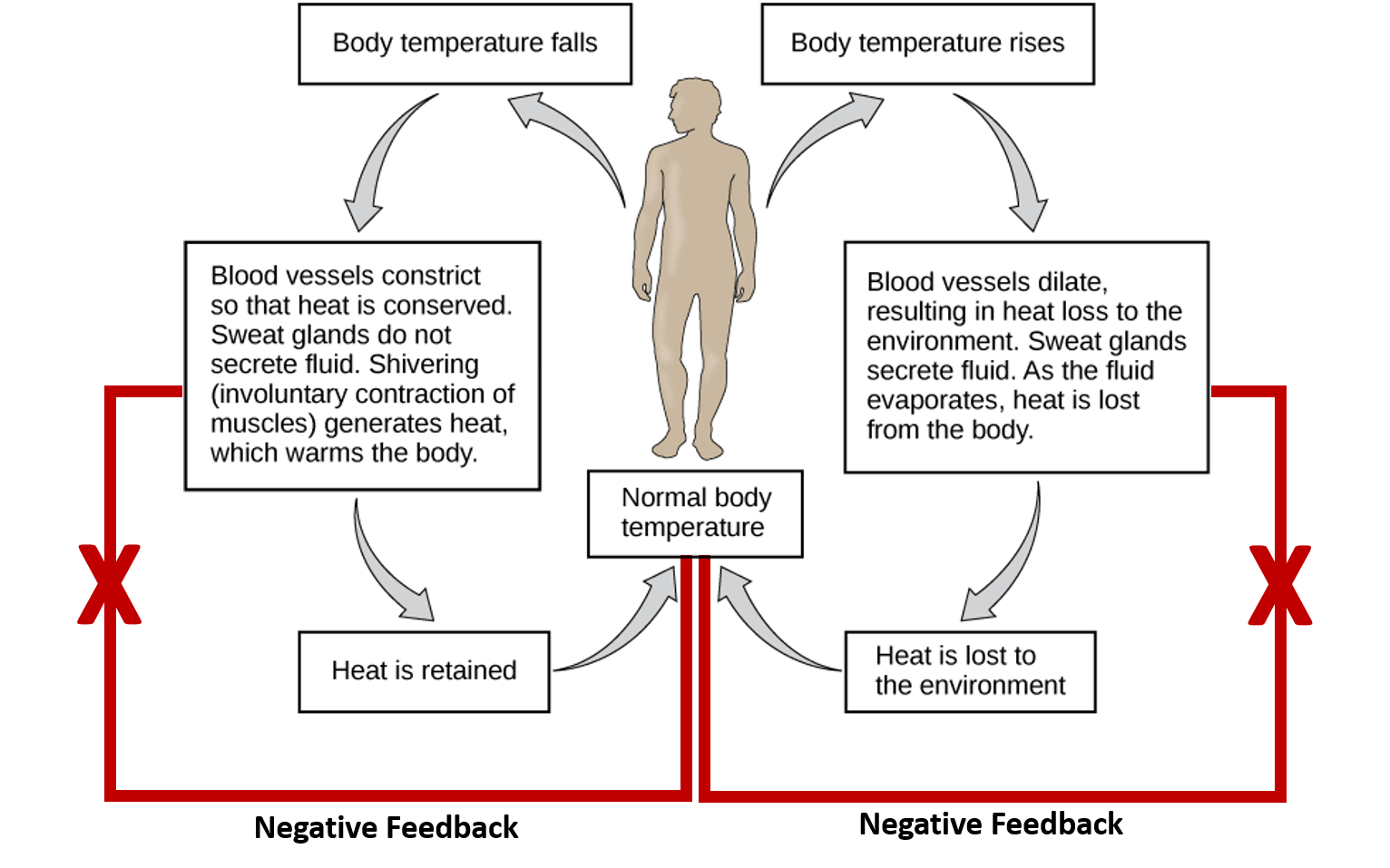
How To Explain Homeostasis An information hypothesis. homeostasis is the ability to maintain a relatively stable internal state that persists despite changes in the world outside. all living organisms, from plants to. Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment by negative or positive feedback mechanisms. learn how sensors, control centers and effectors regulate body parameters such as temperature, blood pressure and glucose levels.

Comments are closed.