How Does Consumer Spending Change During A Recession

What Happens To Consumer Spending During A Recession Borderline. (madonna, 1987) that said, most consumers across the four countries we researched believe that we are in a recession—and say that they are spending more and saving less. (see exhibit 3.) only 18% have seen their income increase in the past six months, and over half believe that they are financially worse off today than they were. There are certain expectations that many economists have about consumer spending in a recession, compared with a boom or recovery. let’s take a look at the relative importance changes in food, vehicles, travel related categories, durable goods, and shelter categories, to see if they match what may be expected intuitively.
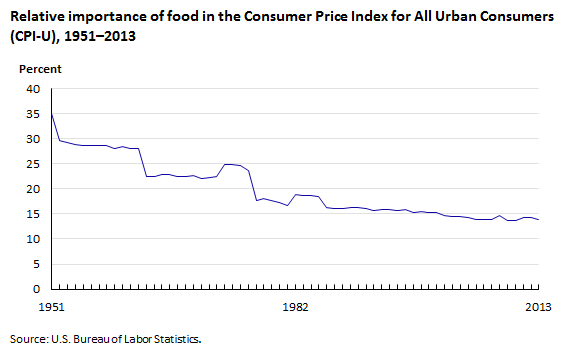
How Does Consumer Spending Change During Boom Recession And Reco We may hypothesize that during a recession, to save money, consumers likely would limit their new car expenditures by buying used cars relative to new cars. indeed, the relative importance of new vehicles dropped dramatically during the recession, falling by about a third. the relative importance of used cars and trucks rose modestly. Consumer spending. one aspect of consumer spending—retail sales—is the total amount of money consumers spend on goods and services. during a recession, retail sales generally decrease as. How spending could change in a recession. when thinking about consumer spending behavior, it’s often contingent on outside factors, and news of immense changes in the economy is worth looking into. below is the distribution of varying consumer decisions and how they'd respond to financial uncertainty or a potential recession in the future. 2. As exhibit 1 shows, food spending as a share of total consumption has been declining over the last few decades: food took up over 20% of total consumption in the late 1970s, compared with just 13.5% as of april 2022. as disposable incomes have risen over time consumers have spent more of their ‘wallet’ on other items, meaning the share of.

In Todayтащs Deep юааrecessionюаб юааconsumerюаб юааspendingюаб On Goods Is Above Pre Pandemic Level How spending could change in a recession. when thinking about consumer spending behavior, it’s often contingent on outside factors, and news of immense changes in the economy is worth looking into. below is the distribution of varying consumer decisions and how they'd respond to financial uncertainty or a potential recession in the future. 2. As exhibit 1 shows, food spending as a share of total consumption has been declining over the last few decades: food took up over 20% of total consumption in the late 1970s, compared with just 13.5% as of april 2022. as disposable incomes have risen over time consumers have spent more of their ‘wallet’ on other items, meaning the share of. Changes in consumer behavior. consumers make trade offs between perceived value and perceived price. normally, the premium brand product would return to favor as the economy bounced back. but the central implication of our research is that even if the willingness of consumers to pay rebounds as the economy does, changes to their perceptions of. On average, consumption grew modestly during previous recessions and, if anything, contributed positively to changes in gdp. in contrast, real private fixed investment, which includes residential investment and business (nonresidential) investment, fell in every recession and tended to be the key driver of gdp declines during recessions.
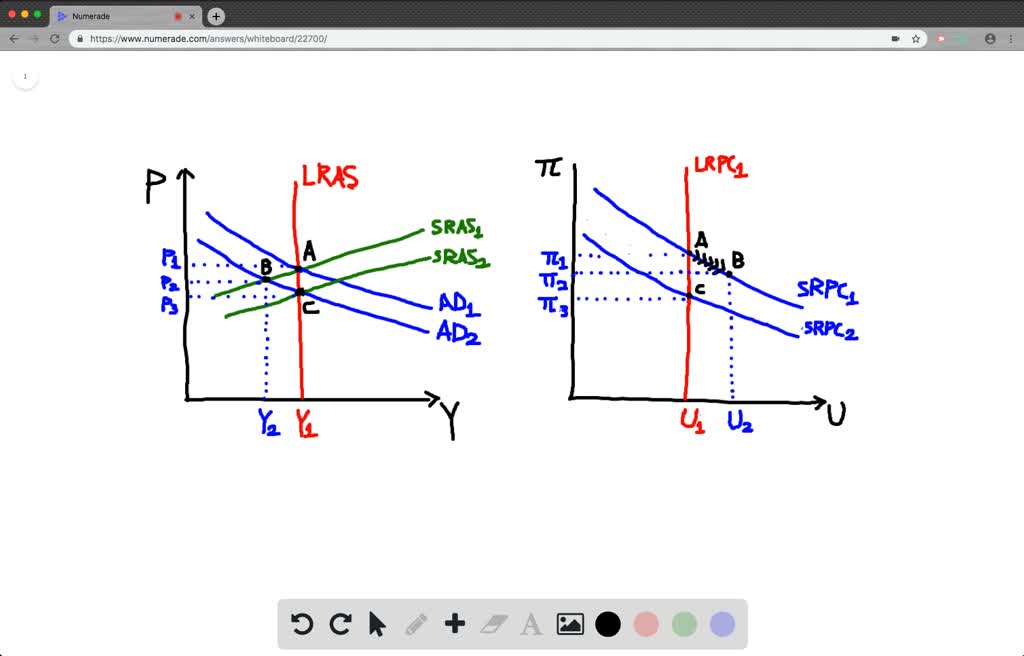
Suppose That A Fall In Consumer Spending Causes A Recession A Illustrate The Immed Changes in consumer behavior. consumers make trade offs between perceived value and perceived price. normally, the premium brand product would return to favor as the economy bounced back. but the central implication of our research is that even if the willingness of consumers to pay rebounds as the economy does, changes to their perceptions of. On average, consumption grew modestly during previous recessions and, if anything, contributed positively to changes in gdp. in contrast, real private fixed investment, which includes residential investment and business (nonresidential) investment, fell in every recession and tended to be the key driver of gdp declines during recessions.

Comments are closed.