Gcse Biology Food Chains Webs And Pyramids
Gcse Biology Food Chains Webs And Pyramids Gcse; wjec; ecosystems – transferring energy – wjec food webs. food chains and webs show the transfer of energy between trophic levels. they can be represented as pyramids of number and. Gcse food webs and food chains. this powerpoint covers most of the gcse level content students need to know from all of the main gcse science courses, including: what a food chain is, the role of plants on a food chain, definitions of terms such as top carnivore, producer and consumer, predator prey cycles, numbering trophic levels in a food.
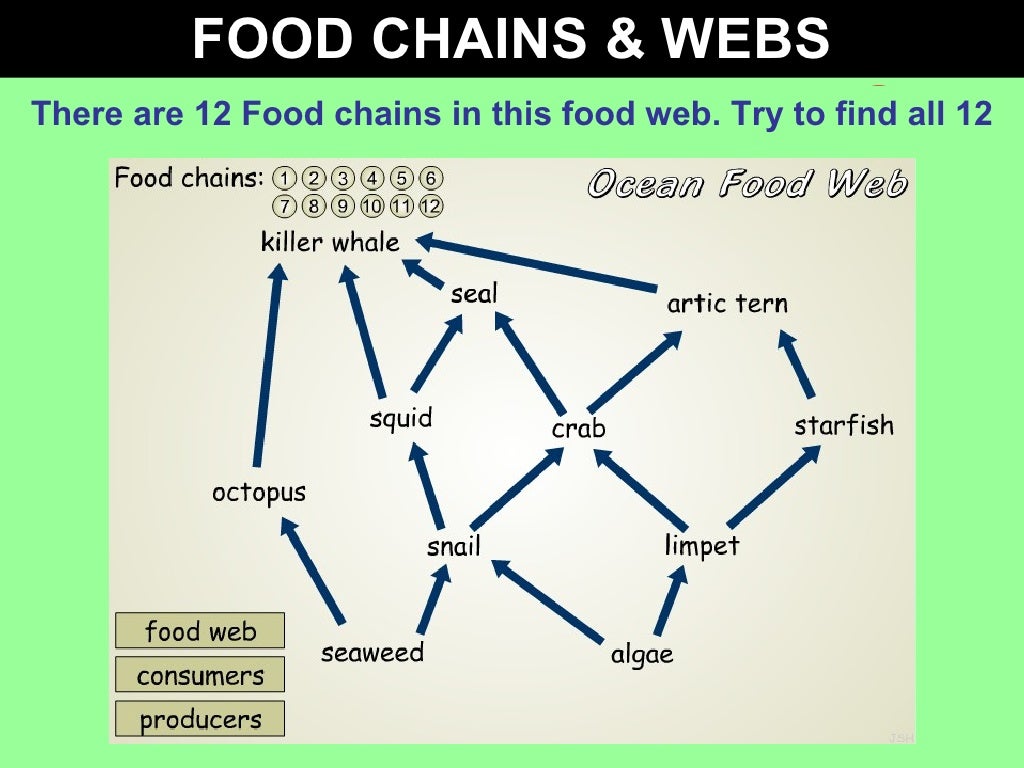
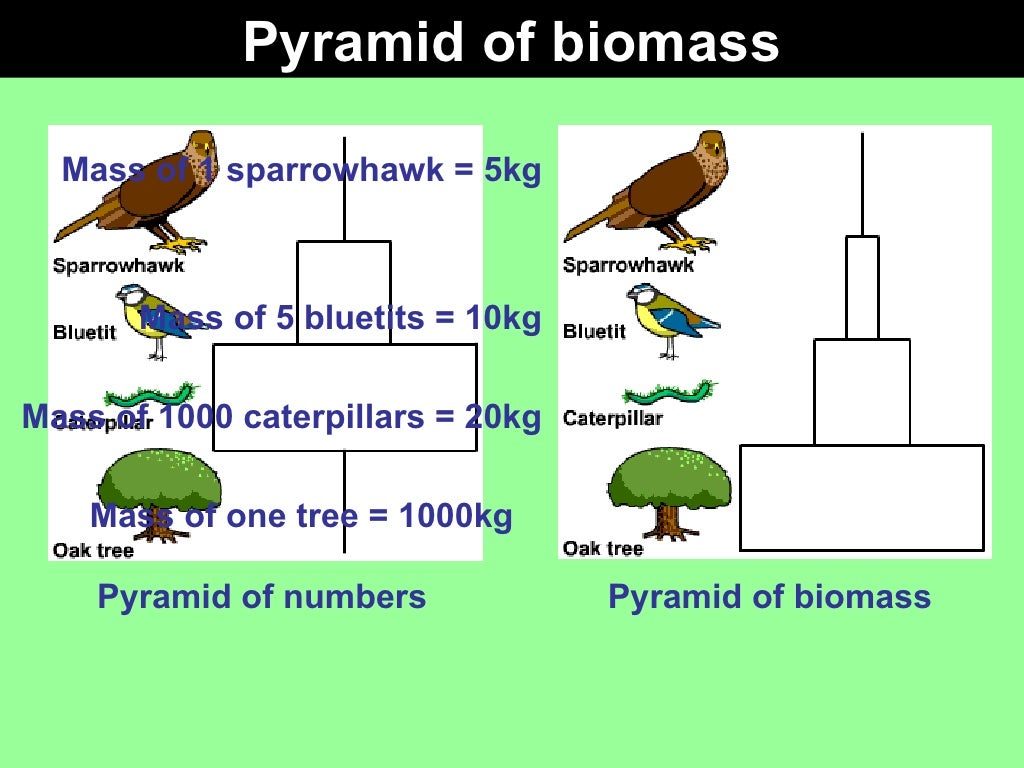
Gcse Biology Food Chains Webs And Pyramids Food chain: determine the linear flow of energy and nutrients from one trophic level to the next. food web: learn about the relationships between creatures and the complexities of trophic interactions. ecological pyramids: examine the distribution of population, biomass, and energy at various trophic levels, and consider the implications for. Learn about how feeding relationships are shown in food chains for gcse biology, aqa. trophic levels close trophic level the position of an organism in a food chain, food web or pyramid. in a. Learn about how feeding relationships are shown in food chains for gcse biology, aqa. are called trophic levels close trophic level the position of an organism in a food chain, food web or. Food chains & webs. food chains show the feeding relationships between living things. pyramids of biomass reveal the mass of living material at each stage in a chain. the amount of material and energy decreases from one stage to the next. food production is more efficient if the food chain is short, or if energy losses from animals are reduced.
Bbc Bitesize Gcse Biology Food Chains Revision 4 Learn about how feeding relationships are shown in food chains for gcse biology, aqa. are called trophic levels close trophic level the position of an organism in a food chain, food web or. Food chains & webs. food chains show the feeding relationships between living things. pyramids of biomass reveal the mass of living material at each stage in a chain. the amount of material and energy decreases from one stage to the next. food production is more efficient if the food chain is short, or if energy losses from animals are reduced. Food chains and food webs are diagrams that show the flow of energy in ecosystems. they show the transfer of energy between organisms present at different trophic levels, e.g. first trophic level. contains producers; organisms that produce their own carbon compounds, e.g. plants use carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose during. Food chains represent the flow of energy and matter within an ecosystem, originating from producers and leading up to the top consumers. producers, such as plants, are always at the start of food chains. these organisms use sunlight or chemicals to create their own food (a process called photosynthesis), hence they are also known as autotrophs.

Gcse Biology Food Chains Webs And Pyramids Food chains and food webs are diagrams that show the flow of energy in ecosystems. they show the transfer of energy between organisms present at different trophic levels, e.g. first trophic level. contains producers; organisms that produce their own carbon compounds, e.g. plants use carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose during. Food chains represent the flow of energy and matter within an ecosystem, originating from producers and leading up to the top consumers. producers, such as plants, are always at the start of food chains. these organisms use sunlight or chemicals to create their own food (a process called photosynthesis), hence they are also known as autotrophs.

Comments are closed.