Consumer Definition Animal

Ecology Consumer Definition Explanation Video Lesson Transcript Study Consumer examples are plentiful, as every animal must consume food in order to live. consumers are grouped into four categories – primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. the category in which an animal is situated is defined by its food source within a specific food chain or food web, and not necessarily by its species or habits. Learn about the different types of consumers in ecosystems, from primary producers to tertiary carnivores. find out how they interact with each other and with decomposers in a trophic pyramid.
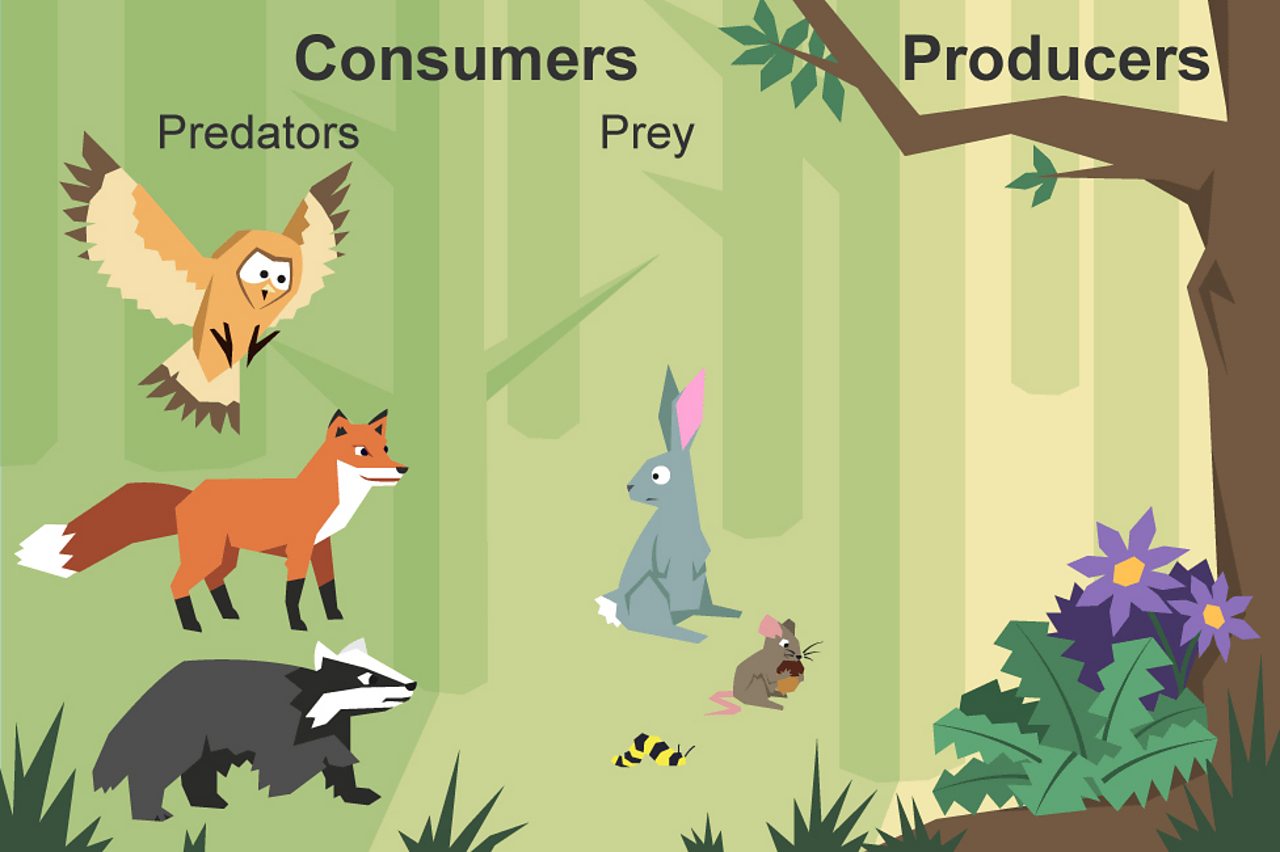
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize Consumer (food chain) a consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually. Primary consumer definition. a primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers. organisms of this type make up the second trophic level and are consumed or predated by secondary consumers, tertiary consumers or apex predators. primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants, which produce their own food. Consumer is a category that belongs inside an ecosystem’s food chain. it primarily refers to animals. consumers cannot generate their own energy and must rely on the intake and digestion of producers, other consumers, or both in order to survive. in food chains, consumers are found alongside two additional groups: producers and decomposers. Primary consumers can range from microscopic organisms like zooplankton to large creatures like elephants. here are some examples. 1. ruminants like giraffes and cows. primary herbivorous consumers such as cows, goats, zebras, giraffes are primary consumers. they consume plant material such as grass, branches, and roots.

Comments are closed.