Consumer And Capital Goods In Production Possibility Frontier
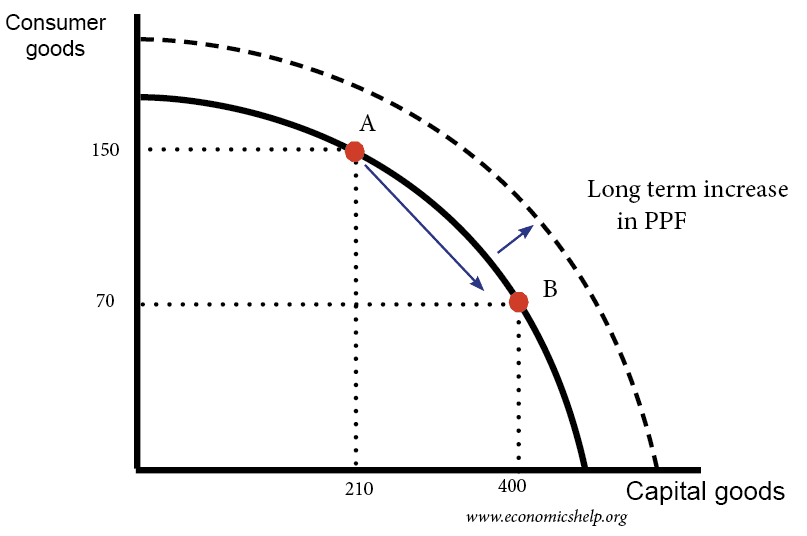
Productive Capacity Economics Help Production possibility frontier and investment. one choice an economy faces is between capital goods (investment) and consumer goods. if more resources are devoted to capital goods (e.g. building new factories) then in the short term, consumption will go down. The production possibility frontier (ppf) is a curve on a graph that illustrates the possible quantities that can be produced of two products if both depend upon the same finite resource for their.

Production Possibility Frontier Definition Curve Example The production possibilities curve (ppc) is a graph that shows all combinations of two goods or categories of goods an economy can produce with fixed resources. take the example illustrated in the chart. this chart shows all the production possibilities for an economy that produces just two goods; robots and corn. Production possibility frontiers are an economic model that shows the maximum potential level of output of two goods that an economy can reach when all its resources are fully in use. they can be used to show the concept of opportunity cost. movements along a ppf. a ppf usually shows an economy with capital goods on the y axis and consumer. A budget constraint shows the different combinations of goods and services a consumer can purchase with their fixed budget. a production possibilities frontier shows the possible combinations of goods and services that a society can produce with its limited resources. the first difference between a budget constraint and a production. The production possibility frontier is an economic model and visual representation of the ideal production balance between two commodities given finite resources. it shows businesses and national economies the optimal production levels of two distinct capital goods competing for the same resources in production, and the opportunity cost associated with either decision.

Comments are closed.