Capital Goods Economics Help

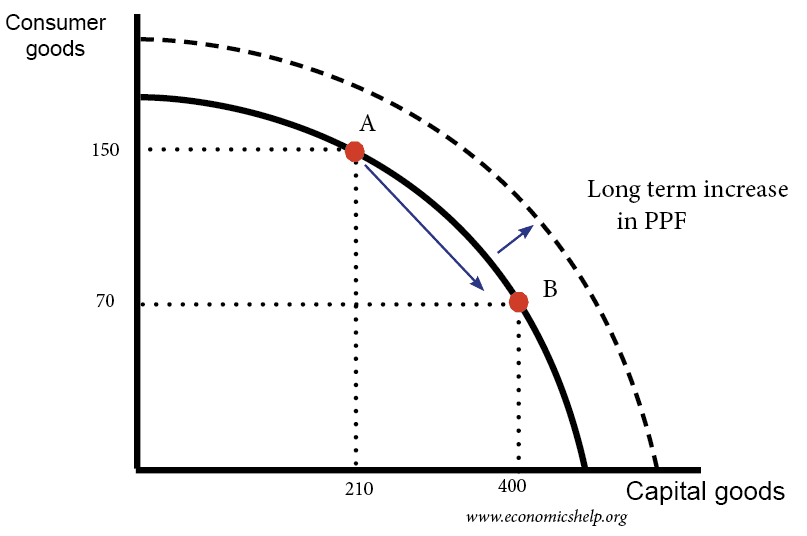
Capital Goods Examples Capital goods are important for increasing the long term productive capacity of the economy. more capital goods reduce consumption in the short term, but can lead to higher living standards in the economy. therefore, economies often face a trade off between consumer goods and capital goods. the opportunity cost of moving from point a to point b. Examples of capital goods. factories or assembly line equipment used to manufacture cars and trucks. machines and technology used to produce goods and services. types of infrastructure, such as.

Capital Goods Economics Help This leads to economic growth. capital goods are also important because they help to create jobs. when businesses invest in capital goods, they need to hire workers to operate and maintain the capital goods. this creates jobs and helps to boost the economy. however, capital goods can also be a burden on the economy. if businesses invest too. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. In economics, capital refers to the assets—physical tools, plants, and equipment—that allow for increased work productivity. in economics, capital goods are the assets that help to. Some examples of capital goods are machines, construction vehicles, furniture, and buildings. all of these capital goods help to drive economic work. capital goods innovations can create new types of manufacturing jobs and drive business growth. when new capital goods are developed, businesses require workers to learn new skills so that they.

Capital Goods Definition Industry Examples How It Works In economics, capital refers to the assets—physical tools, plants, and equipment—that allow for increased work productivity. in economics, capital goods are the assets that help to. Some examples of capital goods are machines, construction vehicles, furniture, and buildings. all of these capital goods help to drive economic work. capital goods innovations can create new types of manufacturing jobs and drive business growth. when new capital goods are developed, businesses require workers to learn new skills so that they. Capital goods don't go straight into the manufacturing of other goods. those goods are called "raw materials." instead, capital goods are part of the process of making other goods or providing services. examples of capital goods include buildings, furniture, and machines like construction vehicles. all of these help drive economic work. Capital goods are the building blocks of production, encompassing tangible assets such as machinery, equipment, and infrastructure. businesses rely on these essential tools to craft consumer goods and offer services. while consumer goods represent the final products that people buy, capital goods are the unsung heroes working behind the scenes.
Capital Goods Economics Help Capital goods don't go straight into the manufacturing of other goods. those goods are called "raw materials." instead, capital goods are part of the process of making other goods or providing services. examples of capital goods include buildings, furniture, and machines like construction vehicles. all of these help drive economic work. Capital goods are the building blocks of production, encompassing tangible assets such as machinery, equipment, and infrastructure. businesses rely on these essential tools to craft consumer goods and offer services. while consumer goods represent the final products that people buy, capital goods are the unsung heroes working behind the scenes.

Comments are closed.