Calculating Class Boundaries And Class Midpoint From A Grouped Frequency Distribution

Calculating Class Boundaries And Class Midpoint From A Grouped Frequency Distribution Youtube 41 – 50. 4. you can find the midpoint of each class by adding the lower class limit and the upper class limit, then dividing by two: class midpoint = (lower class limit upper class limit) 2. the following table shows how to calculate the midpoint of each class: class. frequency. In a frequency distribution, class boundaries are the values that separate the classes. we use the following steps to calculate the class boundaries in a frequency distribution: 1. subtract the upper class limit for the first class from the lower class limit for the second class. 2. divide the result by two. 3.
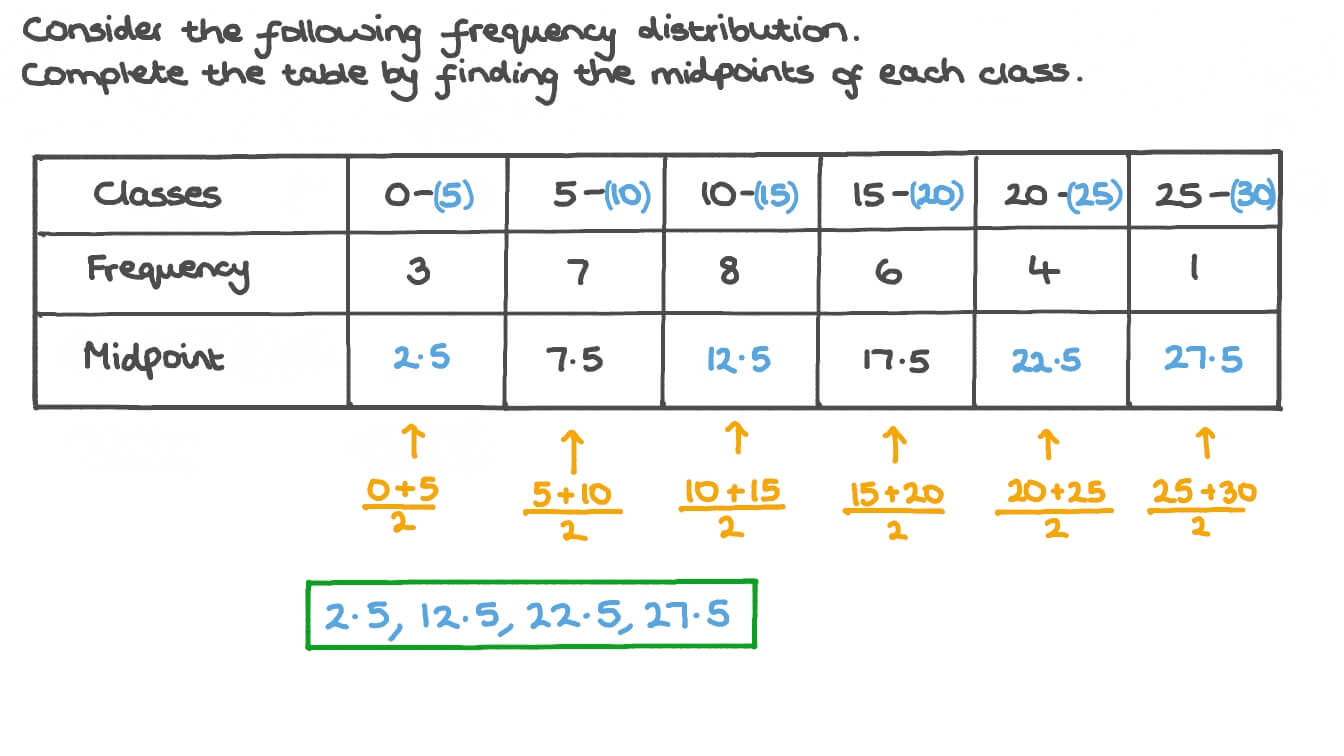
28 Calculate Class Midpoint Tomawarner You can use this grouped frequency distribution calculator to identify the class interval (or width) and subsequently generate a grouped frequency table to represent the data. how to use the calculator: enter the data values separated by commas, line breaks, or spaces. enter the details of the required number of intervals, and click on the. This video will show you how to find class boundaries and class midpoint given a classes. The second class has a lower class boundary of 30.5 and an upper class boundary of 35.5. the third class has a lower class boundary of 35.5 and an upper class boundary of 40.5. and so on. example 2: calculating class boundaries. suppose we have the following frequency distribution: use the following steps to calculate the class boundaries: 1. Summary. for grouped data, we cannot find the exact mean, median and mode, we can only give estimates. to estimate the mean use the midpoints of the class intervals: estimated mean = sum of (midpoint × frequency) sum of frequency. to estimate the median use: estimated median = l (n 2) − b g × w. where:.

Comments are closed.