Basic Networking Commands Explained With Examples Vrogue Co

Basic Networking Commands Explained With Examples Vrogue Co The tracert command prints the path. if all routers on the path are functional, this command prints the full path. if a router is down on the path, this command prints the path up to the last operational router. the tracert command uses the following syntax. tracert destination name or ip address. Basic networking commands (part 1) top 20 linux www vrogue co 10 unix with examples mobile legends command line primer hello i m joni data communication in network 2023 how to add change ip mac address some cmd every windows user should know explained 60 and scripts tools that can help you troubleshoot most issues ipconfig tutorial part 2 {2021} linux unix 5 dev community 35 arp route.
Basic Networking Commands Explained With Examples Vrogue Co The ip command is a unified networking tool for linux systems. the ip command helps view and configure routing, interfaces, network devices, and tunnels. the command is part of the iproute2 package and replaces many older networking tools, such as the route, ifconfig, and netstat commands. syntax. the syntax for the ip command is:. The wide range of linux networking commands can be categorized based on their purpose and use case: status and info: commands like ip, ifconfig, netstat, ss display status and configuration info about network interfaces, connections, routing tables etc. troubleshooting: ping, traceroute, tracepath, mtr help diagnose connectivity and network issues. 5. ss. the ss (socket statistics) command is used to detail about network socket (endpoint for sending and receiving data across the network). to list all the listening and non listening tcp connection, you have to use at option as shown below: ss at. similarly, you can do the same with udp ports using au option:. Networking commands in linux allow users to manage network connections. these commands let users set up networks, fix connection issues, and view network traffic. users can also check network status, change settings, and control network programs with these commands. the commands use basic words that are easy for beginners to understand.

Basic Networking Commands Explained With Examples Vrogue Co 5. ss. the ss (socket statistics) command is used to detail about network socket (endpoint for sending and receiving data across the network). to list all the listening and non listening tcp connection, you have to use at option as shown below: ss at. similarly, you can do the same with udp ports using au option:. Networking commands in linux allow users to manage network connections. these commands let users set up networks, fix connection issues, and view network traffic. users can also check network status, change settings, and control network programs with these commands. the commands use basic words that are easy for beginners to understand. And we can specify the packet size also using the s flag: ping google s 40. we can also specify the next request time using the i flag: ping google i 2. and many more. after executing the above command, hopefully you should be able to find if your system is connected to the internet. This might seem like it's cheating, but in fact, it's a valid network in the sense that a computer needs to know how to address itself. each computer considers itself as the localhost node, with an internal only ip address of 127.0.0.1. you can verify this with the ping command: $ ping c 1 localhost.
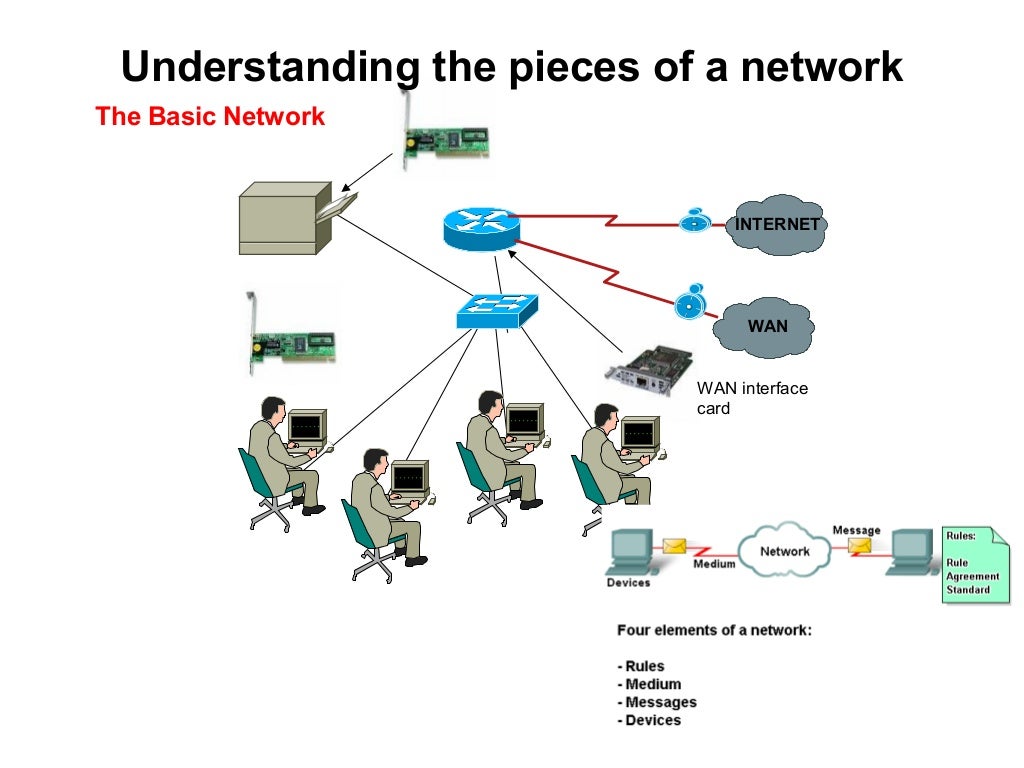
Basic Networking Fundamentals Vrogue Co And we can specify the packet size also using the s flag: ping google s 40. we can also specify the next request time using the i flag: ping google i 2. and many more. after executing the above command, hopefully you should be able to find if your system is connected to the internet. This might seem like it's cheating, but in fact, it's a valid network in the sense that a computer needs to know how to address itself. each computer considers itself as the localhost node, with an internal only ip address of 127.0.0.1. you can verify this with the ping command: $ ping c 1 localhost.

Comments are closed.