Angle In A Circle Theorem
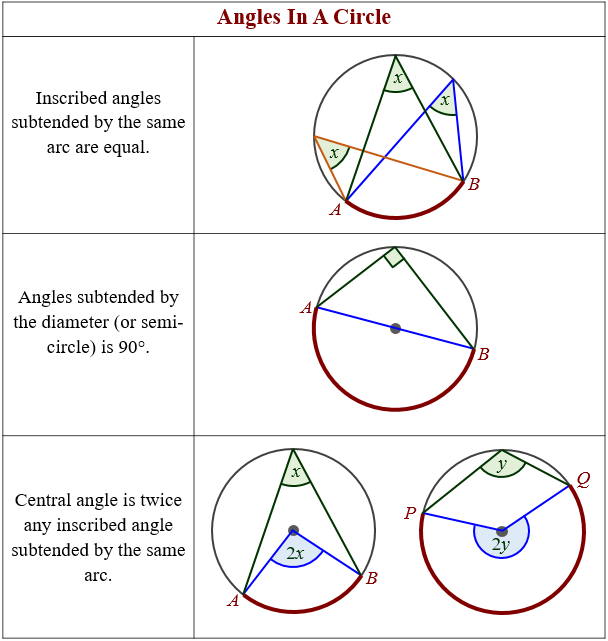
Angles In A Circle Theorems Video Lessons Examples Step By Step Solutions Finding a circle's center. we can use this idea to find a circle's center: draw a right angle from anywhere on the circle's circumference, then draw the diameter where the two legs hit the circle; do that again but for a different diameter; where the diameters cross is the center! drawing a circle from 2 opposite points. Example 2: consider the circle given below with center o. find the angle x using the circle theorems. solution: using the circle theorem 'the angle subtended by the diameter at the circumference is a right angle.', we have ∠abc = 90°. so, using the triangle sum theorem, ∠bac ∠acb ∠abc = 180°.

Circle Theorems Notes вђ Corbettmaths Solved examples on circle theorems. in the circle given below, triangle abc is inscribed in the circle and the tangent de meets the circle at the point b. find the measure of angle “x” and “y.”. solution: we know that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is equal to 180. ∠bac ∠acb ∠abc = 1800. There are seven main circle theorems: alternate segment circle theorem. angle at the centre circle theorem. angles in the same segment circle theorem. angle in a semi circle theorem. chord circle theorem. tangent circle theorem. cyclic quadrilateral circle theorem. below is a summary of each circle theorem, along with a diagram. The central angle of a circle is twice any inscribed angle subtended by the same arc. angle inscribed in semicircle is 90°. an angle between a tangent and a chord through the point of contact is equal to the angle in the alternate segment. the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary. The angle at the centre of a circle is twice any angle at the circumference subtended by the same arc. the following diagrams illustrates the inscribed angle theorem. example: the center of the following circle is o. bod is a diameter of the circle. find the value of x. solution: ∠boc 70˚ = 180˚.
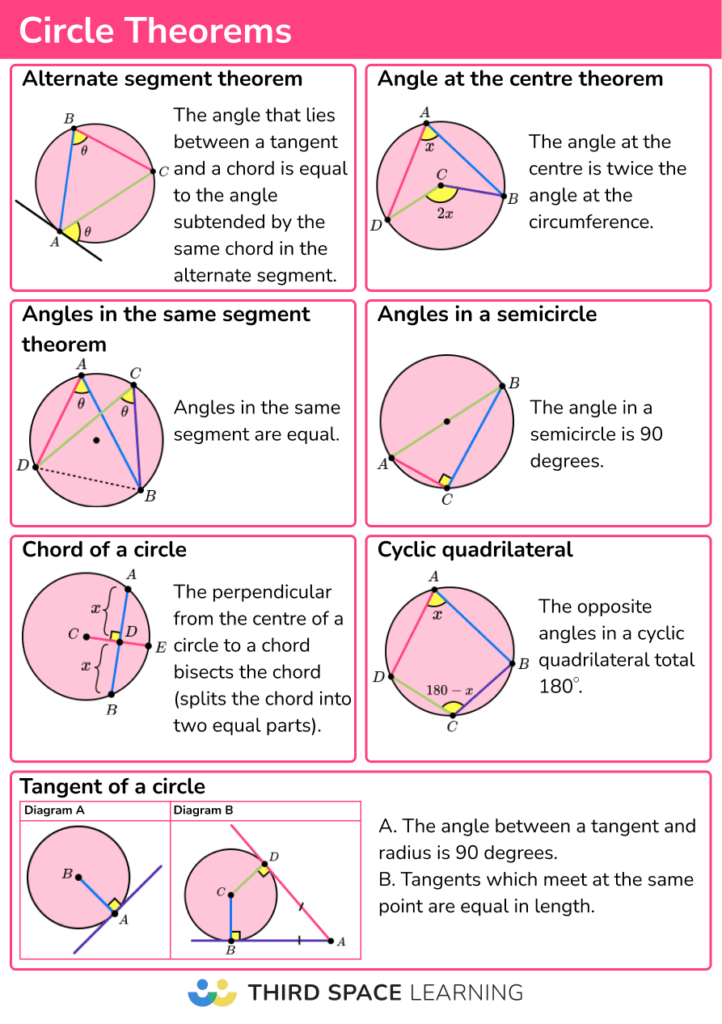
Angles In Circles Geometry The central angle of a circle is twice any inscribed angle subtended by the same arc. angle inscribed in semicircle is 90°. an angle between a tangent and a chord through the point of contact is equal to the angle in the alternate segment. the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary. The angle at the centre of a circle is twice any angle at the circumference subtended by the same arc. the following diagrams illustrates the inscribed angle theorem. example: the center of the following circle is o. bod is a diameter of the circle. find the value of x. solution: ∠boc 70˚ = 180˚. Circle theorems part 1 of 2. the angle between a radius and a tangent is 90 degrees. the angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference. angles in the same segment are equal. the angle in a semi circle is always 90 degrees. the opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral always add up to 180 degrees. show video lesson. Circle theorems higher. circles have different angle properties, described by. theorems. there are seven circle theorems. an important word that is used in circle theorems is. subtend.

Comments are closed.