All Geometry Formulas And Theorems

All Geometry Formulas And Theorems Basic geometry formulas. let us see the list of all basic geometry formulas here. 2d geometry formulas. here is the list of various 2d geometry formulas according to the geometric shape. it also includes a few formulas where the mathematical constant π(pi) is used. perimeter of a square = 4(side) perimeter of a rectangle = 2(length breadth). Chapter 1 basic geometry geometry segments, rays & lines some thoughts about … line segments line segments are generally named by their endpoints, so the segment at right could be named either 𝐴𝐵 $ $ $ $ or 𝐵𝐴 $ $ $ $. segment 𝐴𝐵 $ $ $ $ contains the two endpoints (a and b) and all points on line 𝐴𝐵⃖ , , , ,⃗ that are.
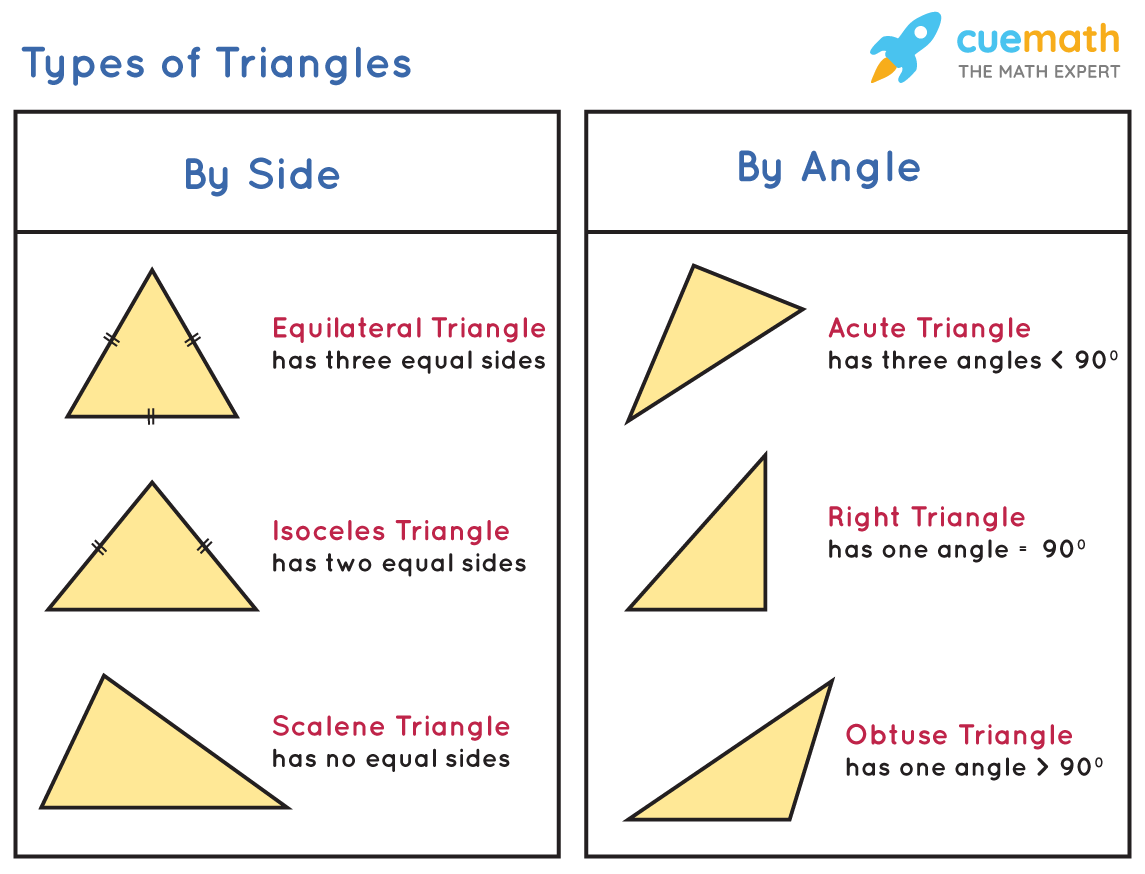
Properties Of A Triangle Formulas Theorems Examples Xy = xz [two sides of the triangle are equal] hence, ∠y = ∠z. where ∠y and ∠z are the base angles. now let’s learn some advanced level triangle theorems. theorem 3: if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the midpoints of the other two sides, then the two sides are divided in the same ratio. Geometry cheat sheet 4 2d shape formulas. cheat sheet 4 contains a range of formulas about 2d shapes: angles in a triangle; pythagoras' theorem; basic trigonometry laws; formulas for the circumference and area of a circle; formula for the length of an arc and the area of a sector;. For example, angles of elevation and depression word problems require the use of the alternate interior angles theorem. the following are examples of angle theorems and postulates: linear pair theorem: if two angles form a linear pair (ie. a straight angle), then the angles are supplementary angles. corresponding angles postulate: if two. Right triangle and pythagora's theorem pythagora's theorem: the two sides a and b of a right triangle and the hypotenuse c are related by a 2 b 2 = c 2. area and perimeter of triangle perimeter = a b c there are several formulas for the area. if the base b and the corresponding height h are known, we use the formula area = (1 2) × b × h.
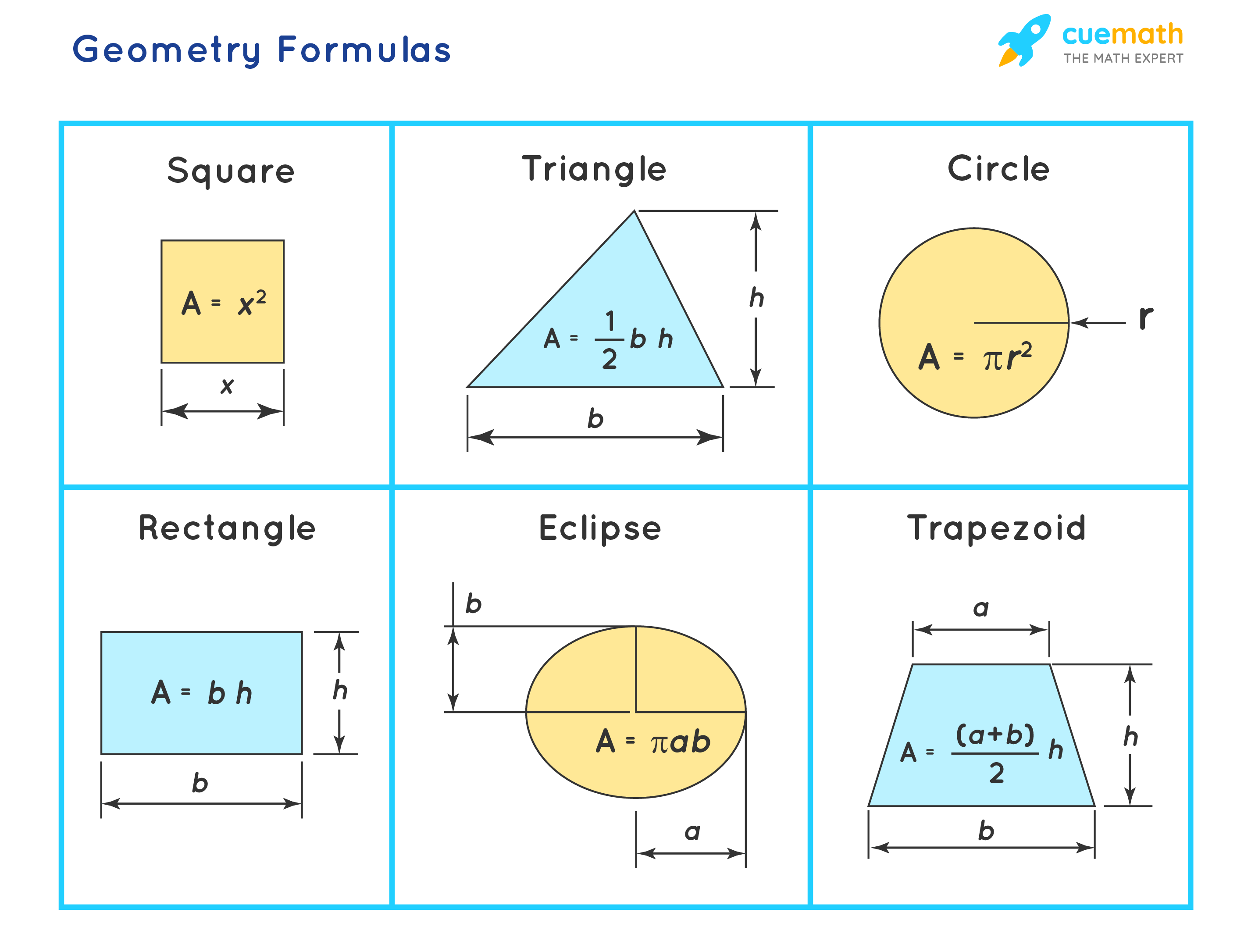
Geometry Formulas All Geometry Formulas 2d And 3d Geometry Fo For example, angles of elevation and depression word problems require the use of the alternate interior angles theorem. the following are examples of angle theorems and postulates: linear pair theorem: if two angles form a linear pair (ie. a straight angle), then the angles are supplementary angles. corresponding angles postulate: if two. Right triangle and pythagora's theorem pythagora's theorem: the two sides a and b of a right triangle and the hypotenuse c are related by a 2 b 2 = c 2. area and perimeter of triangle perimeter = a b c there are several formulas for the area. if the base b and the corresponding height h are known, we use the formula area = (1 2) × b × h. Basic geometry formulas. perimeter of a square = p = 4a. where a = length of the sides of a square. perimeter of a rectangle = p = 2 (l b) where, l = length ; b = breadth. area of a square = a = a 2. where a = length of the sides of a square. area of a rectangle = a = l×b. where, l = length ; b = breadth. Circle formulas and theorems. circumference: c = 2πr or π d, where r is the radius of the circle and d is its diameter. area: area circle = π r2. arc length: the length of an arc (part of the circumference) is equal to the circumference of the circle (2π r) times the fraction of the circle represented by the arc.

Formulas In Geometry Basic geometry formulas. perimeter of a square = p = 4a. where a = length of the sides of a square. perimeter of a rectangle = p = 2 (l b) where, l = length ; b = breadth. area of a square = a = a 2. where a = length of the sides of a square. area of a rectangle = a = l×b. where, l = length ; b = breadth. Circle formulas and theorems. circumference: c = 2πr or π d, where r is the radius of the circle and d is its diameter. area: area circle = π r2. arc length: the length of an arc (part of the circumference) is equal to the circumference of the circle (2π r) times the fraction of the circle represented by the arc.
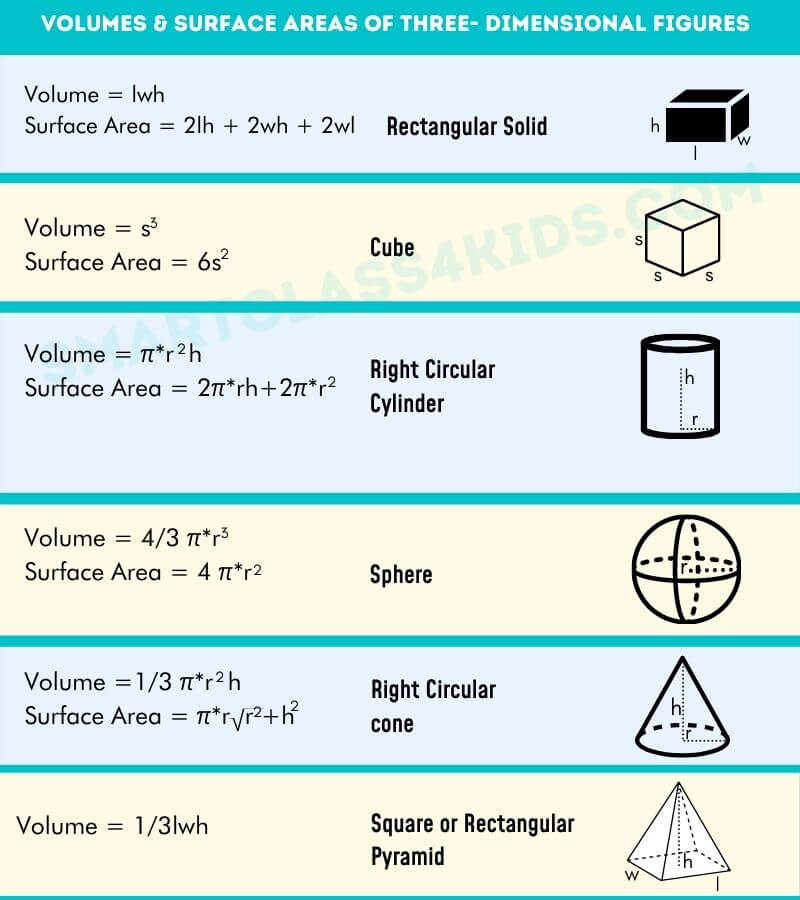
Basic Geometry Formulas Area Perimeter Volume

Comments are closed.