20 Basic Networking Commands Part 1 Tracert 180 101 50 242 Csdnеќље ў

20 Basic Networking Commands Part 1 Tracert 180 101 用于看计算机是否可以连接上某ip,输入ping 180.101.50.242。. 可以追踪到数据包从本机到目标ip经过的中间设备的ip。. 输入 tracert 180.101.50.242。. 用于查询域名服务器,可以看到域名对应的ip地址。. 输入命令help color。. 输入命令ipconfig。. To display the arp cache entry for a specific ip address, specify the ip address with the n option. for example, the following command displays the arp cache table for the interface that is assigned the ip address 192.168.42.171. arp a n 192.168.42.171. the following image shows the output of the above command.
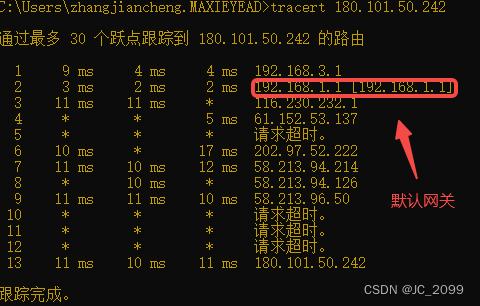
20 Basic Networking Commands Part 1 Tracert 180 101 Tracert <ip address> trace route to a specific ip address. to trace the route to a specific ip address, for example 72.47.244.140, type the following in the command window then press enter: tracert 72.47.244.140. it can take a few minutes for the trace to complete. if you wish to abort a trace, press ctrl c on your keyboard. In most cases, you'll see the ip address, but if reverse dns lookup is successful, it displays the hostnames, which can help identify routers by name. to trace the path to the host named microsoft and prevent the resolution of each ip address to its name, type: copy. tracert d microsoft . The command syntax is simple, type the ip address or domain name of the remote server you want to trace route to: tracert example.local. you will see an output similar to the following, where tracert lists all the hops (network devices) it traverses on its way to reach the remote server. trace route in windows. Tracert d: tells tracert not to resolve addresses to host names; tracert h: maximum hops – lets you change the default number of hops, e.g. h 30; tracert j host list: specifies the lsr (loose source route) along the host list w timeout: lets you set how long tracert waits at each hop before considering it a timeout. e.g.
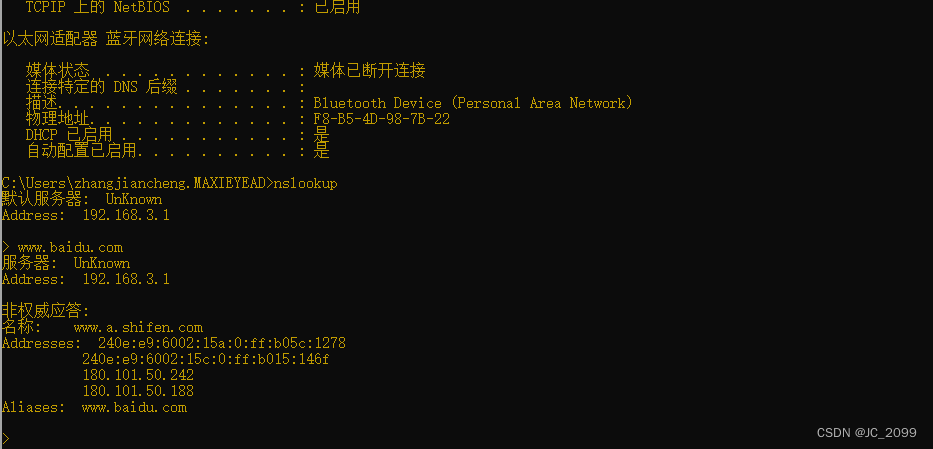
20 Basic Networking Commands Part 1 Tracert 180 101 The command syntax is simple, type the ip address or domain name of the remote server you want to trace route to: tracert example.local. you will see an output similar to the following, where tracert lists all the hops (network devices) it traverses on its way to reach the remote server. trace route in windows. Tracert d: tells tracert not to resolve addresses to host names; tracert h: maximum hops – lets you change the default number of hops, e.g. h 30; tracert j host list: specifies the lsr (loose source route) along the host list w timeout: lets you set how long tracert waits at each hop before considering it a timeout. e.g. 7 – nslookup. nslookup is a command line networking tool used for querying domain name system (dns) to obtain domain name or ip address mapping, or other dns records. nslookup has two modes: interactive and non interactive. the windows version of nslookup is available as part of the microsoft networking tools. 12. tracert used for: troubleshooting network connection issues. command to enter: tracert. by using the tracert command you can trace the route a packet takes before reaching its destination, and see information on each “hop” along the route. a hop refers to the number of routers that a packet passes through along its route.

20 Basic Networking Commands Part 1 Tracert 180 101 7 – nslookup. nslookup is a command line networking tool used for querying domain name system (dns) to obtain domain name or ip address mapping, or other dns records. nslookup has two modes: interactive and non interactive. the windows version of nslookup is available as part of the microsoft networking tools. 12. tracert used for: troubleshooting network connection issues. command to enter: tracert. by using the tracert command you can trace the route a packet takes before reaching its destination, and see information on each “hop” along the route. a hop refers to the number of routers that a packet passes through along its route.

Comments are closed.